Installation and Operational Instructions for
EAS
®
-smartic
®
s
ynchronous clutch Type 48_._ _5._
Sizes 01
– 2
(B.4.17.1.GB)
25/11/2011 TK/NU/SU
Chr. Mayr GmbH + Co. KG
Tel.: +49 8341 804-0
Eichenstraße 1
Fax: +49 8341 804-421
D-87665 Mauerstetten
http://www.mayr.com
Page 12 of 18
Germany
E-Mail:
Torque Adjustment
In order to guarantee low-wear clutch operation, it is essential to
adjust the torque to a sufficiently high service factor (overload
torque to operating torque). Our experience has shown that an
adjustment factor of 1,3 to 3 gives good results.
For very high load changes, high accelerations and uneven
operation, please set the adjustment factor higher.
The respective torque adjustment range is printed on the
Adjustment Table (11). Torque adjustment is carried out by
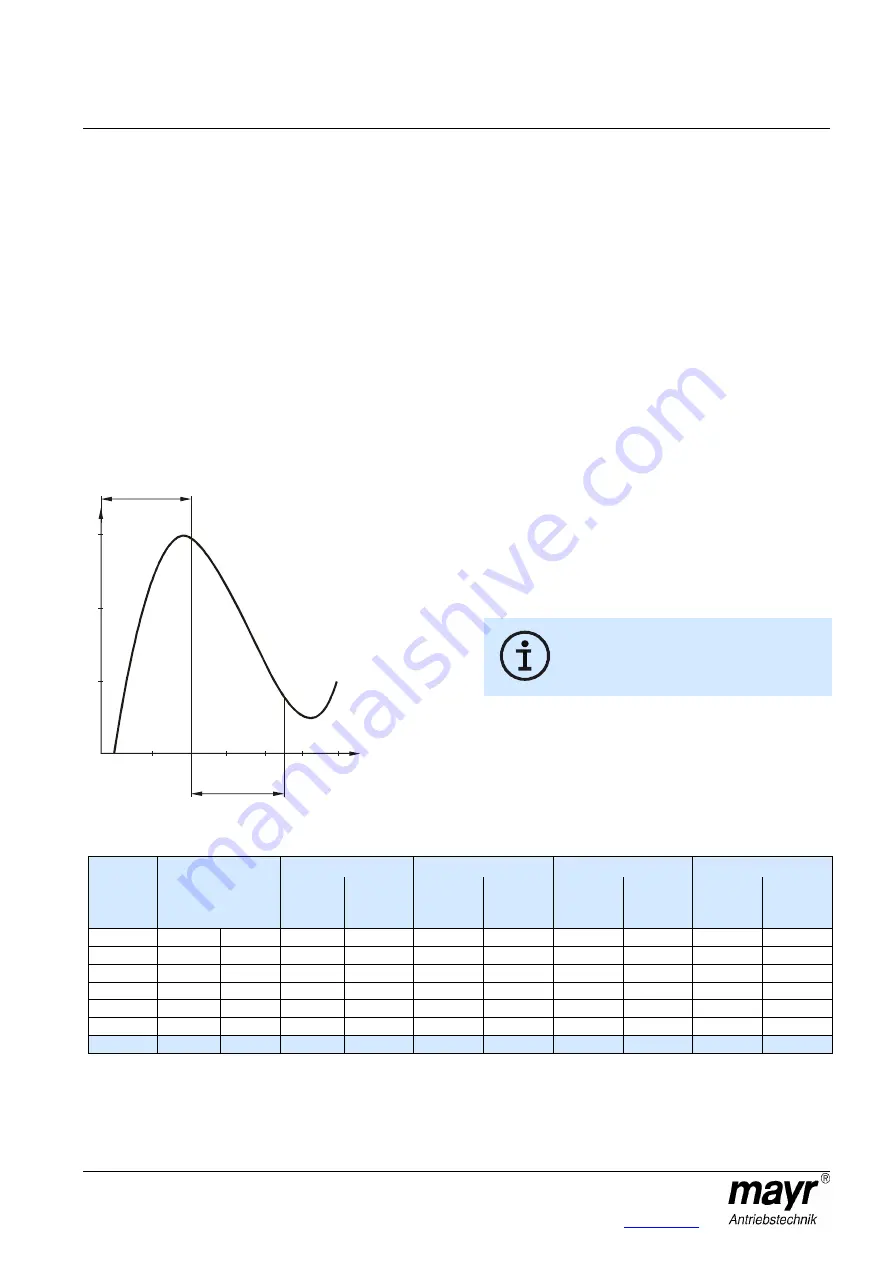
turning the adjusting nut (5/20). The installed cup springs (10)
are operated in the negative range of the characteristic curve
(see Fig. 14). This means that tightening the adjusting nut
(5/20) causes the spring force to decrease, and loosening the
adjusting nut (5/20) causes the spring force to increase.
If no torque is specified on order, the clutch is pre-set to
approx. 80 % of the maximum torque. The reference marking
and the torque specification show the set value directly.
If no changes to the pre-set clutch torque are required
customer-side, the hexagon head screws (6/22) must
nevertheless be screwed out, painted with Loctite 243 and
screwed back in again by the customer.
Fig. 14
Cup Spring Layering
Correct cup spring layering is a prerequisite for problem-free
clutch function and torque adjustment.
On all Sizes, 7 torque ranges (see Table 3) are possible.
Changing the Torque
On clamping ring hub designs
Type 48_._35._
and Type 48_._45._
In order to adjust the torque to a different value, simply
1. loosen and unscrew the hexagon head screw (6),
2. adjust the adjusting nut (5) using a hook wrench until the
reference marking shows the required torque value,
3. if necessary, correct the adjusting nut (5) position slightly
until the marking notches between the clamping ring hub
(1/1.1) and the adjusting nut (5) align, and
4. paint the hexagon head screw (6) with Loctite 243 before
screwing it back in again.
On key design Type 48_._25._
In order to adjust the torque to a different value, simply
1. loosen and unscrew the hexagon head screw (22),
2. adjust the adjusting nut (20) using a hook wrench until the
reference marking shows the required torque value,
3. if necessary, correct the adjusting nut (20) position slightly
until the marking notches between the locking ring (21) and
the adjusting nut (20) align, and
4. paint the hexagon head screw (22) with Loctite 243 before
screwing it back in again.
Adjusting the adjusting nut (5/20) or distorting
the cup springs (10) outside of the cup spring
characteristic curve (see Fig. 14) stops the
clutch functioning.
Table 3: Cup Spring Layering and Torque Ranges
Size 01
Size 0
Size 1
Size 2
Type
Cup spring
layering
3)
[Nm]
Graduation
lines for
M = 80 %
[Nm]
Graduation
lines for
M = 80 %
[Nm]
Graduation
lines for
M = 80 %
[Nm]
Graduation
lines for
M = 80 %
48_.2_5._
1x1 times 1 \ /////// 7
2,7
– 5
19
5
– 10
21
10
– 20
16
20
– 40
25
48_.3_5._
1x2 times 2 \\ ////// 6
5
– 10
19
10
– 20
22
20
– 40
17
40
– 80
26
48_.4_5._
1x3 times 3 \\\ ///// 5
8
– 15
20
15
– 30
23
30
– 60
19
60
– 120
28
48_.5_5._
1x4 times 4 \\\\ //// 4
11
– 20
20
20
– 40
23
40
– 80
19
80
– 160
28
48_.6_5._
1x6 times 6 \\\\\\ // 2
18
– 33
20
35
– 65
24
70
– 125
20
140
– 250
30
48_.7_5._
1x8 times 8 \\\\\\\\ 0
32
– 40
21
60
– 80
27
120
– 160
25
240
– 320
32
48_.8_5._
4)
1x8 times 8 \\\\\\\\ 0
35
– 60
24
70
– 120
31
150
– 240
25
300
– 500
35
3)
Example:
On Type 481.425.0, the cup spring layering is 1x3 times, which means that three cup springs are engaged thrust washer-side
and five cup springs are not engaged (adjusting nut-side) => 3 \\\ ///// 5.
4)
Types 48_.8_5._ require a special pressure flange as well as a special thrust washer.
Path to
operating range
F
o
rc
e
F
Graph of
spring characteristic
curve
Operating
range
Spring path S


















