Installation and Operational Instructions for BRE250 and BRE400
ROBA-stop
®
-M brake Type 891.
0_ _._
Sizes 250 and 500
(E070 09 203 001 4 EN)
31/10/2019 TK/MW
Chr. Mayr GmbH + Co. KG
Eichenstraße 1, D-87665 Mauerstetten, Germany
Phone: +49 8341 804-0, Fax: +49 8341 804-421
Page 17 of 20
your reliable partner
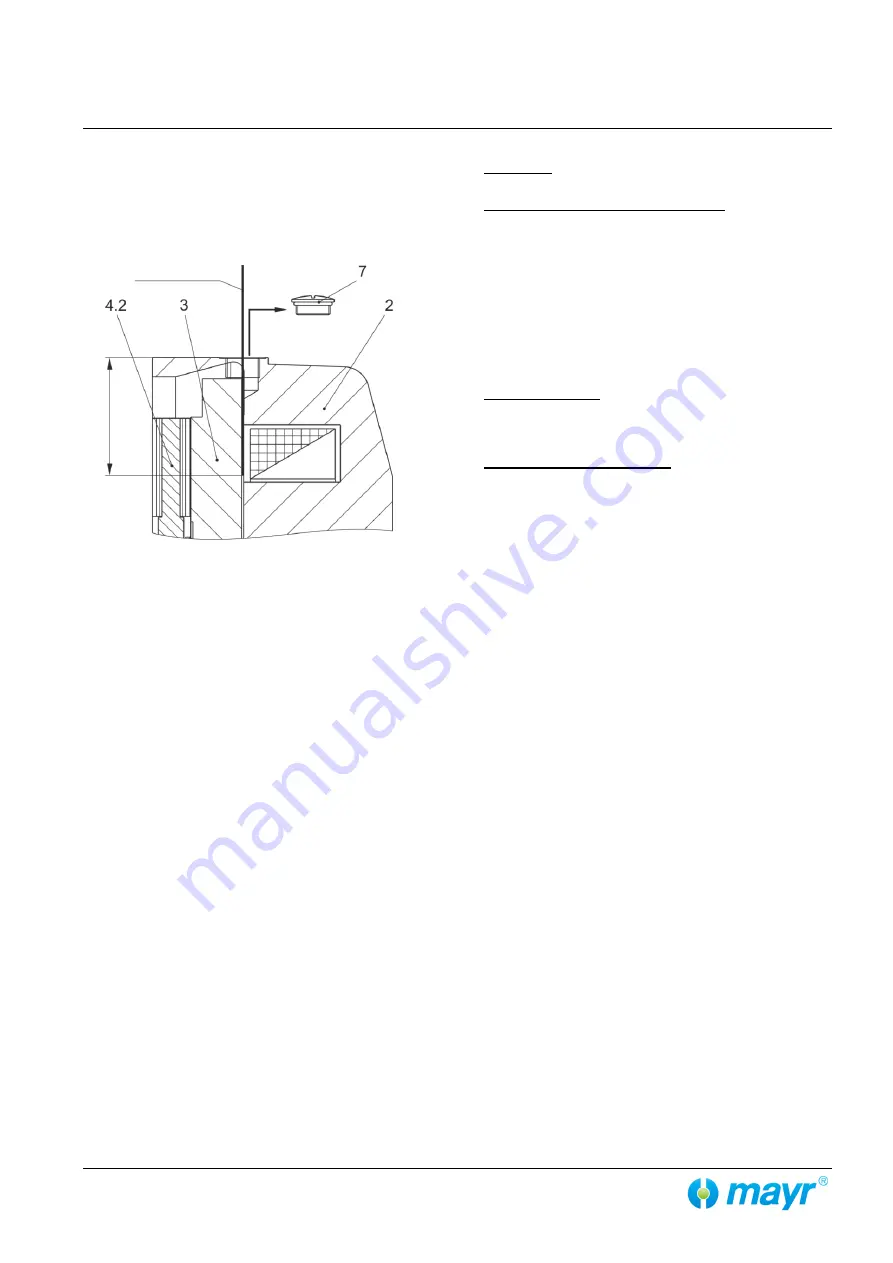
Air Gap Inspection
The air gap can be inspected via a feeler gauge after removing
the sealing plug / screw plug (7). The feeler gauge must be in-
serted at least 40 mm deep (see Fig. 10), so that the distance
between the armature disk (3) and the coil carrier (2) can be
measured.
Fig. 10
Maintenance
The amount of wear on the rotor (4) must be examined during the
regular inspection intervals:
ROBA-stop
®
-M
brakes are mainly maintenance-free.
The friction lining pairing is robust and wear-resistant. This en-
sures a particularly long service lifetime of the brake. The friction
lining is subject to functional wear in case of
EMERGENCY
STOP
and during regular conditioning of the friction lining pair-
ing.
In addition to this, further signs of wear may appear:
Dry-running wear due to the presence of residual friction in
the brake.
Increased wear (depending on speed) in the case of a verti-
cal or pivoting installation position for the motor axis, partic-
ularly to the lower friction lining.
If the rotor (4) does become worn due to the high total friction
work, and the function of the brake can no longer be guaranteed,
the brake can be re-set to its functional state by replacing the ro-
tor.
The quality of the counter friction surface must be checked.
The wear condition of the rotor (4) can be specified by:
Checking the air gap (see above).
Max. permitted air gap see Table 1.
Measuring the rotor thickness on the dismantled brake.
See Table 1 for the minimum rotor thickness.
We recommend the following regular inspection intervals:
Once a year
Inspection of the air gap “a”.
Twice a year or after 1000 operating hours
Inspection of the rotor thickness (wear).
Inspection of the toothing of the rotor (4) and hub (1) for
ease of movement, increased backlash, and damage.
Max. permitted torsional backlash of the rotors on the
hub
0.3°.
Inspection on an engaged brake and load-free output by
turning the motor shaft.
Inspection of the armature disk (3), the intermediate disk (10)
and the customer flange for plane parallelism and wear (ex-
cessive formation of scoring).
Clean the brake.
Replacing the rotors
After having reached the maximum air gap.
In safety-critical applications (without cyclical brake test) at
the latest after 6 years of operating the system
User-implemented determination
The frequency of the friction lining pairing conditioning and the
torque inspection must be determined by the user depending on
the application.
In order to maintain the brake torque in holding applications, the
friction lining pairing must be conditioned regularly. This must be
carried out in the form of dynamic braking procedures. After-
wards, the brake torque must be checked.
If regular brake conditioning in holding applications is not possi-
ble, a higher level of security must be used for dimensioning
(recommendation: Si = 2.0 => Please observe: The dynamic di-
mensioning must be taken into account separately).
Wear times are influenced by many factors and can vary substan-
tially. The required inspection and maintenance intervals must be
calculated individually according to the system manufacturer's
planning documentation.
Feeler gauge
min.
40 mm


















