3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 18 -
3.5 Digital Main Processor (AD6525, U100)
(1) Architecture Overview
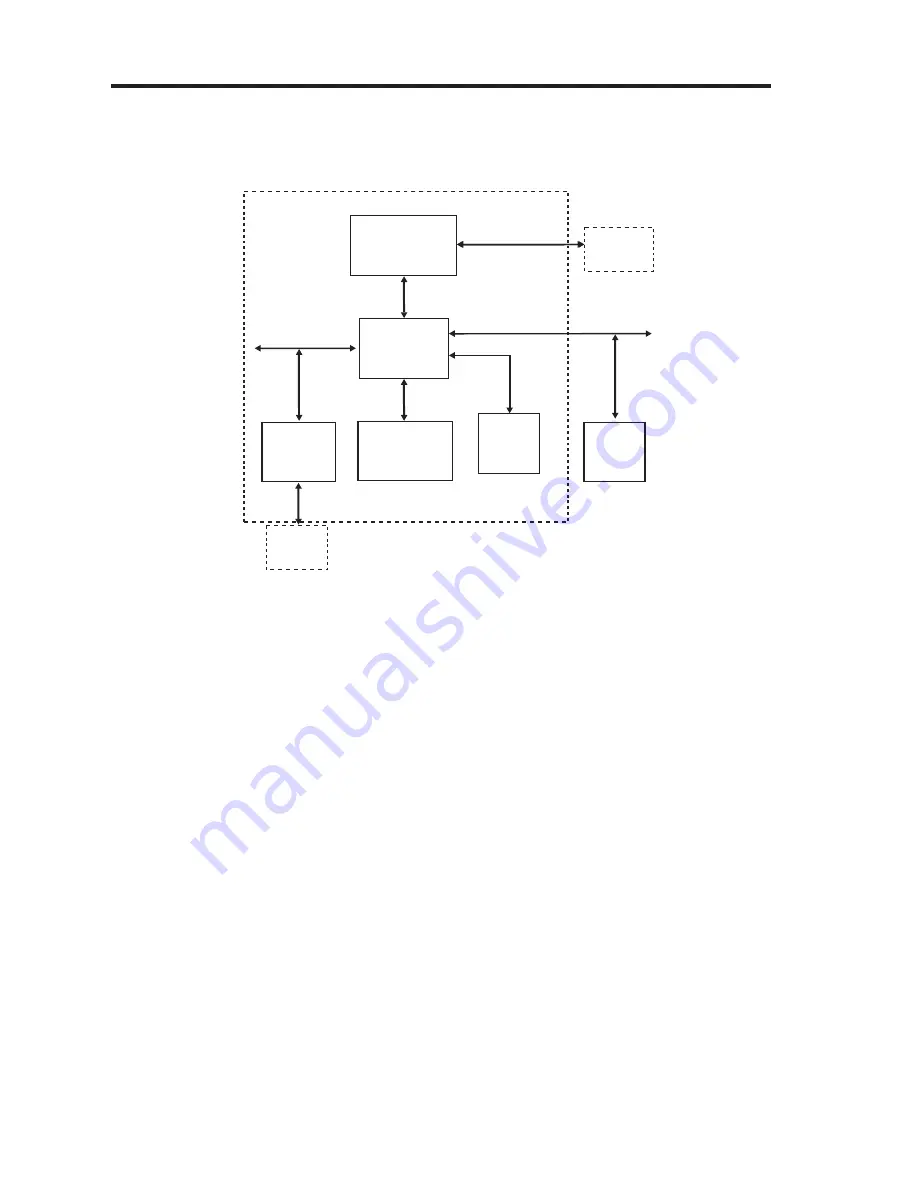
Figure 3-8 Block Diagram of the AD6525 Internal Architecture
AD6525
@C5410
(VBC)
CRE
RQ@L
EK@RG
MMI
USC
LTB
Odqhogdq`k
RF-Control
Subsystem
Subsystem
Subsystem
(ARM7TDMI
®
)
CL@`mcATR
@QAHSQ@QHNM
Serial Link
DSP BUS
RBUS
EBUS
PBUS
SBUS
The internal architecture of AD6525 is shown in Figure 3-8. AD6525 regroups three main subsystems
connected together through a dynamic and flexible communication bys network. It also includes onboard
system RAM (SRAM) and interfaces with external Flash Memory, Baseband converter functions, and
terminal functions like MMI, SIM and Universal System Connector (USC).
The Digital Signal Processing (DSP) subsystem primarily hosts all the speech processing, channel
equalization and channel codec functions. The code used to implement such functions can be stored in
external Flash Memory and dynamically downloaded on demand into the DSP’s program RAM and
Instruction Cache.
The microcontroller subsystem supports all the GSM terminal software, including the layer 1, 2 and 3 of
the GSM protocol stack, the MMI, and applications software such as data services, test and
maintenance. It is tightly associated with onchip system SRAM and also includes boot ROM memory
with a small dedicated routine to facilitate the initialization of the external Flash Memory via code
download using the on-chip serial interface to the external Flash Memory interface.
The peripheral subsystem is composed of system peripherals such as interrupt controller, real time
clock, watch dog timer, power management and a timing and control module. It also includes peripheral
interfaces to the terminal functions:
keyboard, battery supervision, radio and display. Both the DSP and the MCU can access the peripheral
subsystem via the peripheral bus (PBUS).
For program and data storage, both the MCU subsystem and the DSP subsystem can access the on
chip system SRAM and external memory such Flash Memory.The access to the SRAM module is made
through the RAM Bus (RBUS) under the control of the bus arbitration logic. Similarly, access to the Flash
Memory is through the
parallel External Bus (EBUS).
Summary of Contents for G1610
Page 1: ...Service Manual Model G1610 Service Manual G1610 P N MMBD0045701 Date February 2005 Issue 1 0 ...
Page 52: ...4 TROUBLE SHOOTING 51 Graph 4 14DCS TX Graph 4 15EGSM TX VC1 VC2 VC1 VC2 VC1 VC2 VC1 VC2 ...
Page 70: ...5 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION 69 5 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION Figure 5 1 Figure 5 2 ...
Page 71: ...5 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION 70 Figure 5 3 Figure 5 4 ...
Page 72: ...5 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION 71 Figure 5 5 ...
Page 73: ...5 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION 72 Figure 5 6 1 3 2 4 Figure 5 7 1 2 3 ...
Page 74: ...5 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION 73 Figure 5 8 4 2 3 1 2 1 Figure 5 9 ...
Page 75: ...5 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTION 74 Figure 5 10 ...
Page 86: ...7 BLOCK DIAGRAM 85 7 BLOCK DIAGRAM Power supply ...
Page 87: ... 86 ...
Page 108: ...12 AUTO CALIBRATION 107 12 3 Equipment Setup Figure 12 1 Equipment Setup ...
Page 111: ...12 AUTO CALIBRATION 110 ...
















































