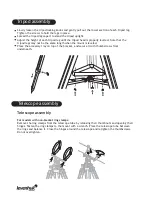
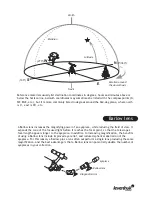
Sky conditions are usually defined by two atmospheric characteristics, seeing, or the steadiness
of the air, and transparency, light scattering due to the amount of water vapor and particles in
the air. When you observe the Moon or planets, and they appear as though water is running over
them, you probably have bad "seeing" because you are observing through turbulent air. In
conditions of good seeing, the stars appear steady, without twinkling. Ideal transparency is when
the sky is inky black and the air is unpolluted
Observations
Travel to the best site that is reasonably accessible. It should be away from city lights, and
upwind from any source of air pollution. Always choose as high an elevation as possible; this will
get you above some of the lights and pollution and will ensure that you aren't in any ground fog.
Sometimes low fog helps by blocking light pollution if you get above it. Try to have an
unobstructed view of the horizon, especially the southern horizon if you are in the Northern
Hemisphere and vice versa. Remember that the darkest sky is usually at the zenith, directly
above your head. Do not try to observe anything that passes near hills or buildings along its
route. Even extremely light winds can cause major air turbulence as they flow over the top of a
building or a wall. When observing from a pavement, your steps may cause slight tremors and
vibrations of the telescope. Pavements may also be exuding heat stored throughout the day,
which will also decrease the quality of your views. Observing through a window is not
recommended because the window glass will distort images considerably. And an open window
can be even worse, since warmer indoor air will escape out the window, causing turbulence
which also affects images. All in all, astronomy is an outdoor activity. These telescope models
need at least 10 minutes in the open to adapt to the outside temperatures.
Choosing the right time for observations
The best conditions will have still air, and obviously, a clear view of the sky. Some clouds may be
present, as often broken clouds provide excellent seeing. Do not view immediately after sunset.
After the sun goes down, the ground is still cooling, causing air turbulence. As the night goes on,
not only will the seeing improve, but air pollution and ground lights will often diminish as well.
The best time for observations is early morning. Objects are best observed as they cross the
meridian, which is an imaginary line that runs through the Zenith, due North-South. This is the
point at which objects reach their highest points in the sky, and negative atmospheric effects are
reduced to their minimum.
Eye adaptation
Try to avoid any electric lights for 30 minutes prior to observing. This allows your pupils to dilate
to their maximum diameter. To avoid fatigue, observe with both eyes open. It is recommended to
cover the eye you are not using with your hand or an eye patch. Use peripheral vision on dim
objects, as the center of your eye is the least sensitive to low light levels. When viewing a dim
object, don't look directly at it. Instead, look slightly to the side, and the object will appear
brighter.
Weather conditions