14
7. Measurement Principle
7-1 Principle of Earth Resistance Measurements
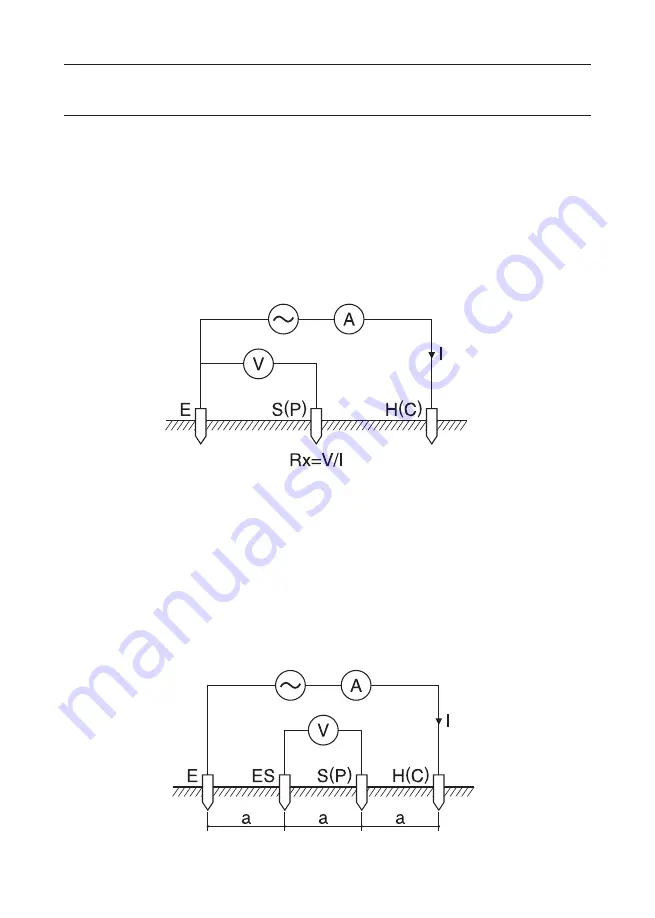
This instrument makes earth resistance measurements with fall-of-potential
method, which is a method to obtain earth resistance value Rx by applying
AC current I between the measurement object E (earth electrode) and
H(C) (current electrode), and finding out the potential difference V between
E (earth electrode) and S(P) (potential electrode). This unit outputs test
voltage Um to generate AC current I . Earth resistance value Rx is
determined by the AC current I and potential difference V . See Fig. 3.
7-2 Principle of Earth Resistivity (ρ) Measurements
According to the Wenner 4-pole method, apply AC current I between the
E (earth electrode) and H(C) (current electrode) to find out the potential
difference V between the potential electrode S(P) and auxiliary earth
electrodes ES . (Fig.4)
To obtain the earth resistance Rg(Ω) , devide the potential difference V
by AC current I ; where the interval between electrodeds is a (m). Then
use a formula: ρ= 2・π・a・Rg(Ω・m)
Fig. 3
Fig.
4
















































