5
No.
Fr q [Hz]
No.
Frq [Hz]
No.
Frq [Hz]
No.
Frq[Hz]
186.2
1
67.0
11
94.8
21
131.8
31
192.8
2
69.3
12
97.4
22
136.5
32
203.5
3
71.9
13
100.0
23
141.3
33
210.7
4
74.4
14
103.5
24
146.2
34
218.1
5
77.0
15
107.2
25
151.4
35
225.7
6
79.7
16
110.9
26
156.7
36
233.6
7
82.5
17
114.8
27
162.2
37
241.8
8
85.4
18
118.8
28
167.9
38
250.3
9
88.5
19
123.0
29
173.8
39
10
91.5
20
127.3
30
179.9
and are sent to VCO to change VCO oscillation frequency to the
preset value, and then VCO is locked.
N=FVCO/FR
N
:
Frequency demultiplication times
FVCO
:
VCO oscillation frequency
FR
:
Reference frequency
Check Loss of Lock: When PLL is in loss of lock, IC pin14 sends out
low level signal to MCU, which controls the transmitter not to
transmit and initiate warning tome.
3.5 Voice Indication Circuit
The radio features voice indication, which is very useful at night or
in the environment of dim light.
MCU stores the voice indication of channels. If Channel
Annunciation function has been activated, every time you change
the channel, the speaker will sound voice annunciation of the
current channel number.
3.6 Power Supply
The radio is equipped with 7.4V, 1200mAh Li-Ion battery. The
battery supplies power directly to the transmitter amplifier circuit
(Q103, Q104) and the receiver amplifier (IC401). The power supply
of other circuits is the regulated 5V power.
IC502: 5V low voltage difference, micropower regulator, together
with Q10, and Q30 supply big current 5V power to the whole radio.
Q502: T5V switch, controlled by MCU.
T5V: Supplies power for the front terminal of the transmitter.
Q505: R5V switch, controlled by MCU.
R5V: Supplies power for the receiver RF amplification, mixing, IF
processing, audio signal processing.
Q503: C5V switch, controlled by MCU
C5V: The 5V power controlled by power saving supplies power for
the frequency synthesizer.
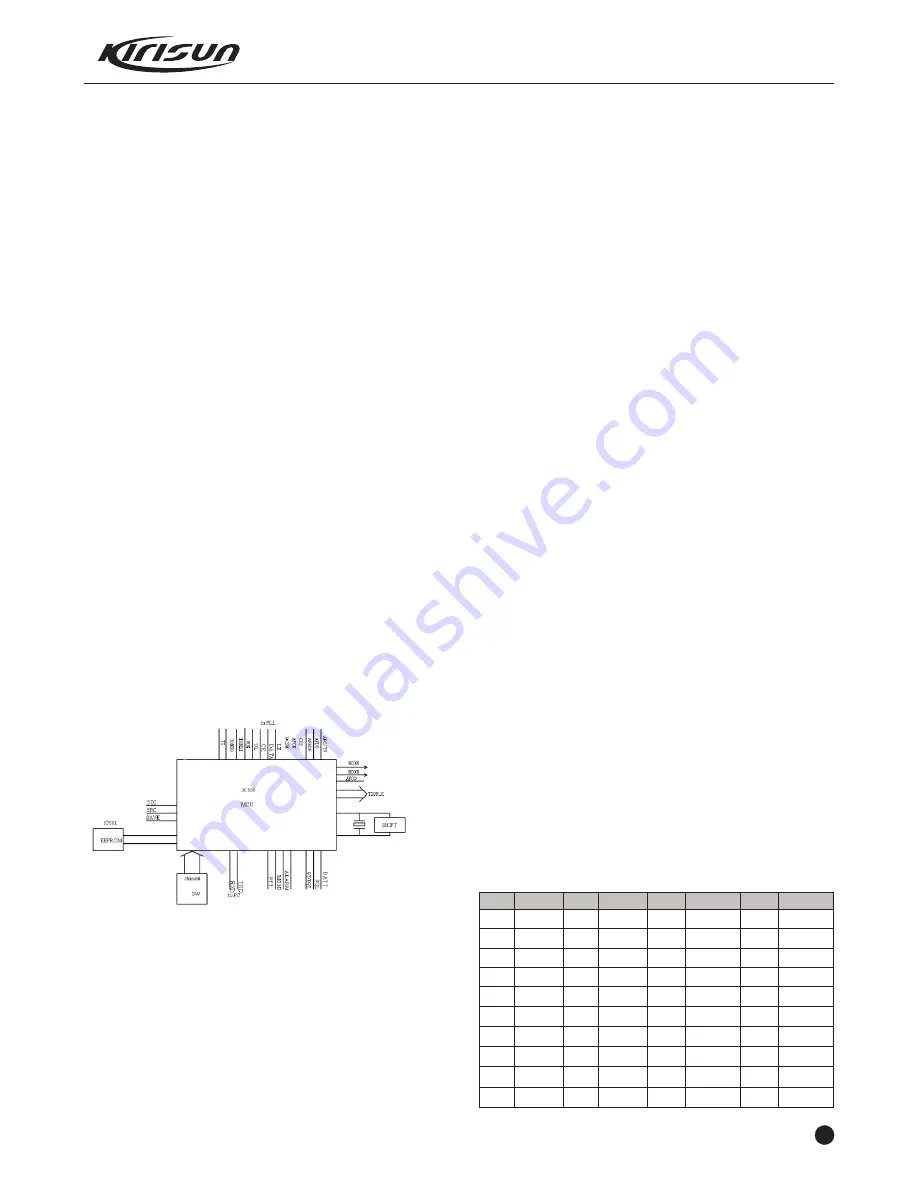
3.7 MCU
Figure 3.11 MCU Diagram
MCU controls the working of each location of the radio to realize all
the radio functions.
Connects with the PC
Accesses the radio status data
Controls PLL to generate the receiving and transmitting local
oscillation frequency.
Accesses the current channel status.
Controls the LED status indication
Controls the power supply of each location
Checks the action of each function key
Generates content of voice indication
Generates Power-On Indication Tone
Generates CTCSS/DCS signals
Generates 2-Tone/5-Tone signals
Generates power control signals
CTCSS/DCS decoding
2-Tone/5-Tone decoding
Squelch check and control
Samplings VOX level
Controls audio processor to conduct audio emphasis/de-emphasis,
scrambler/descrambler, compander, filter and amplification.
2
Memorizer
(
E PROM
,
AT24C64
)
Memorizes the radio channel data, CTCSS/DCS data, and other
data of function setting and parameter adjustment.
CTCSS/DCS Encoding and Decoding
CTCSS/DCS signals generated by MCU (output form pin20 and
pin26, PWM wave) are filtered at the filter circuit and then sent to
VCO and TCXO for modulation.
CTCSS/DCS signals from the receiver are sent to MCU for
demodulation. MCU determines whether the signals contain the
same CTCSS/DCS as that set on the radio and decides whether to
turn on the speaker.
Power Adjustment
MCU PIN2 sends DC signals to APC to control the transmitter
output power.
CTCSS
CTCSS (continuous tone control squelch system) is a squelch
control system modulated on carrier wave with continuous subaudio
frequency as pilot frequency. If a channel is set with CTCSS, only
when both the CTCSS of the receiver and that of the transmitter are
identical, communication is available, which avoids interference of
other signals.
39 groups of standard CTCSS frequency is available on the radio,
see Table 3.1.
CTCSS signals generated by MCU (PWM wave) pass the low pass
filter consisting of RC to be filtered off the high frequency over
300Hz and then are sent to VCO for modulation.
PT5200 SERVICE MANUAL







































