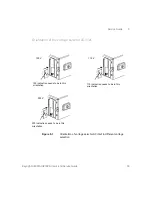
3
Operations and Features
46
Keysight U8001A/U8002A User’s and Service Guide
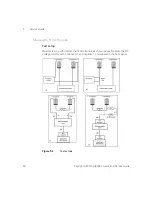
Extending the Voltage and Current Range
Two or more power supplies can be connected in series or parallel to extend the
range of voltage and current. This may serve as a lower cost alternative to a
power supply with higher power rating.
Series connection
Serial connection of two or more power supplies can achieve the output isolation
rating of any one supply to obtain a higher voltage than a single power supply.
Power supplies connected in series can be operated with one load across both
power supplies or with a separate load for each power supply. The power supply
has a diode with reverse polarity connected across the output terminals to avoid
any damages when operated in series with other power supplies. It will be
protected if the load is short-circuited, or when one of the power supply is turned
on separately in a series-connected power supplies.
When serial connection is used, the output voltage is the sum of output voltage
across all power supplies, while the output current is the output current from an
individual power supply. Each power supply must be adjusted to obtain the total
output voltage.
Parallel connection
Two or more power supplies which are capable of constant voltage or constant
current automatic cross-over operation can be connected in parallel to obtain a
total output current greater than one power supply. Total output current is the
sum of output current across all power supplies. The output settings from each
power supply can be made separately. The control of output voltage for one of the
power supply should be set to the desired output value, while the other power
supply should be set to a slightly higher output voltage. The power supply with
higher output voltage setting will deliver its constant current output and drop its
output voltage. This will happen until the output voltage equals the output of the
other supply, and the other supply will remain in constant voltage operation; only
delivering that fraction of rated output current that is necessary to fulfill the total
load demand.