IP Phone User Manual
20
/
42
KT101 is connected supports this function. Otherwise, your KT101 may be unable to obtain
a network address, or you cannot place calls.
IV.
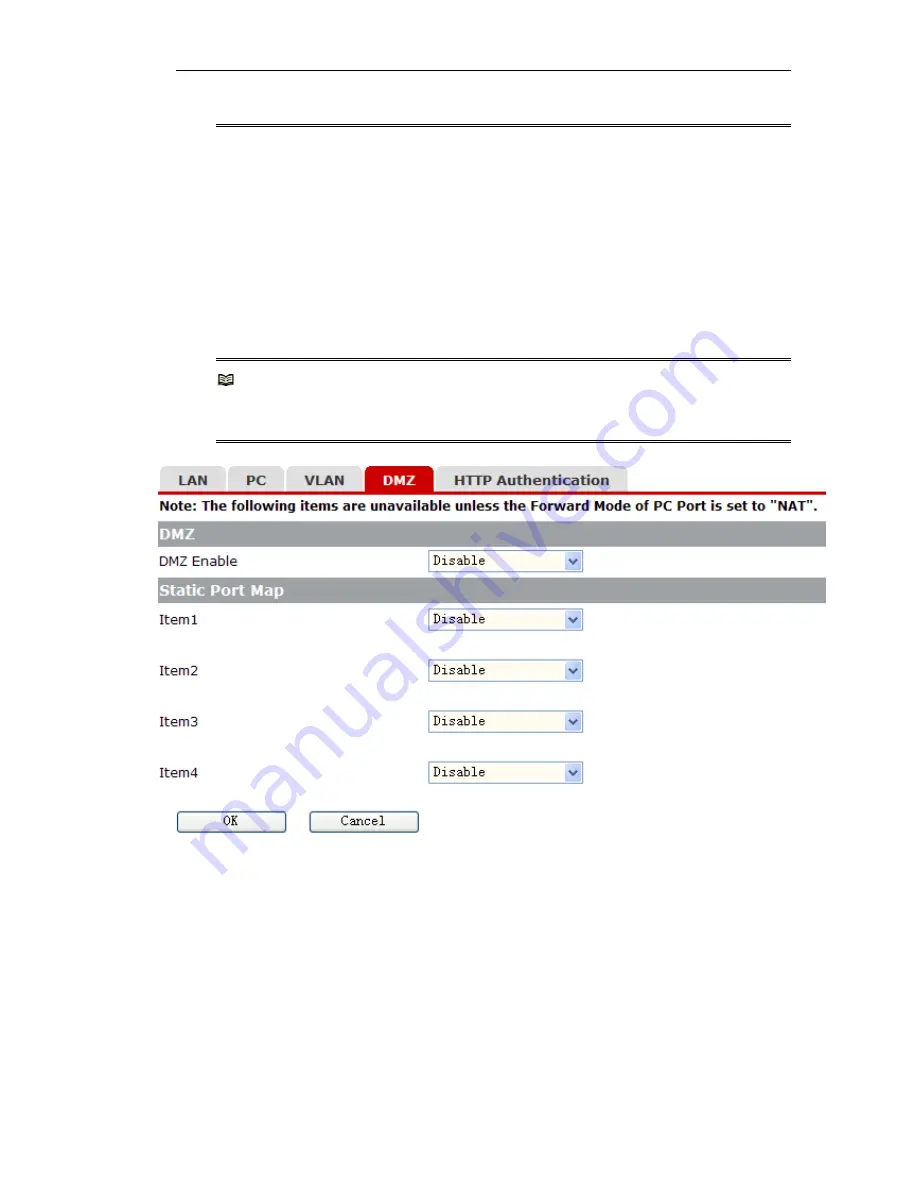
Configuring DMZ and static port mapping
When operating in NAT mode, your KT101 denies requests initiated from external IP
networks. But some implementations require accessing the PC connected to the PC
interface of your KT101 from external networks to utilize the services provided by the
PC. In this case, you can satisfy the requirement by enabling static port mapping or
DMZ function.
Click the [DMZ] tab. The DMZ and static port map page appears (as shown in Figure
3-9), displaying items for setting the DMZ and static port mapping functions.
Note:
The configurations described below about DMZ and static port mapping are necessary only
when the forwarding mode is set to NAT.
Figure 3-9 Web configuration
– DMZ and Static Port Map
1) Configuring DMZ
With the DMZ function enabled, you can specify a port number range. Packets
destined for the LAN interface of your KT101 with destination port numbers within
this range are forwarded to the corresponding ports of the host that is connected to
the PC interface of your KT101. (The host herein is referred to as a DMZ host.)
When you select Enable from the [DMZ Enable] drop-down list to enable the DMZ
function, the related configuration items appear, as shown in Figure 3-10.






























