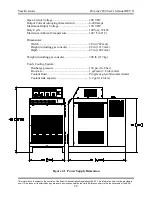
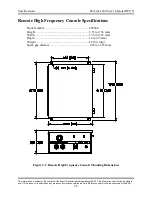
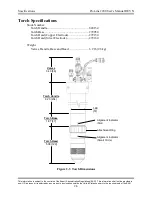
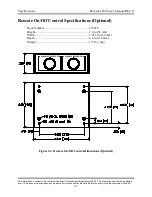
Safety
ProLine 2200 User’s Manual REV N
This information is subject to the controls of the Export Administration Regulations [EAR]. This information shall not be provided to
non-U.S. persons or transferred by any means to any location outside the United States contrary to the requirements of the EAR.
1-1
Section 1 Safety
General Precautions
Whereas plasma cutting has been used safely for years, it does require certain precautions
to ensure the safety of the operator and other people around the equipment. It is
management’s responsibility to see that the following safety information is provided to
each person who will operate, observe, perform maintenance, or work in close proximity
to this piece of equipment.
Installation, as well as repairs, made to the ProLine 2200 system should only be
performed by qualified personnel. The ProLine system makes use of both A.C. and D.C.
circuitry for operation.
Fatal shock hazard does exist. Exercise extreme caution
while working on the system
.
Ultraviolet Radiation Protection
Plasma cutting produces ultraviolet radiation similar to a welding arc. This ultraviolet
radiation can cause skin and eye burns. For this reason, it is essential that proper
protection be worn. The eyes are best protected by using safety glasses or a welding
helmet with an AWS No. 12 shade or ISO 4850 No. 13 shade, which provides protection
up to 400 amperes. All exposed skin areas should be covered with flame-retardant
clothing. The cutting area should also be prepared in such a way that ultraviolet light
does not reflect. Walls and other surfaces should be painted with dark colors to reduce
reflected light. Protective screens or curtains should be installed to protect additional
workers in the area from ultraviolet radiation.
Noise Protection
The ProLine 2200 system generates high noise levels while cutting. Depending on the
size of the cutting area, distance from the cutting torch, and arc current cutting level,
acceptable noise levels may be exceeded. Proper ear protection should be used as
defined by local or national codes. See Section 2 for noise emission levels.
Toxic Fume Prevention
Care should be taken to ensure adequate ventilation in the cutting area. Some materials
give off toxic fumes that can be harmful or fatal to people in the vicinity of the cutting
area. Also, some solvents decompose and form harmful gases when exposed to
ultraviolet radiation. These solvents should be removed from the area prior to cutting.
Galvanized metal can produce harmful gases during the cutting process. Ensure proper
ventilation and use breathing equipment when cutting these materials.
Certain metals coated with or containing lead, cadmium, zinc, beryllium, and mercury
produce harmful toxins. Do not cut these metals unless all people subjected to the fumes
wear proper air breathing equipment.