JOHNSON CONTROLS
60
FORM 100.50-NOM6
ISSUE DATE: 8/07/2017
SECTION 4 – MAINTENANCE
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE – THREE TO SIX
MONTHS
Disconnect and lock-out power from the
unit anytime service is being performed
on the fan section. Failure to do so could
result in serious injury or death due to the
fan turning ON while work is in progress.
Squealing belts during starting is caused
by slipping belts that are not tensioned
properly.
Motor Bearing Lubrication
Bearings must be re-lubricated periodically to assure
long life. Motor bearing should be lubricated yearly,
but may need lubrication more frequently, depending
on severe operating conditions.
Belt Tension
Adjust the belt tension if necessary. Required belt ten-
sion data is supplied on the fan “skid” data plate, at-
tached to the fan housing. Never use a belt dressing
on the belts. If belts slip with the proper tension, use a
good grade of belt cleanser to clean the belts.
Refer to
Figures 24.
Never use excessive belt tension,
as this could result in damaging
the bearing, motor pulleys or motor
base. See drive label on fan housing
adjacent to drive for specific details on
tension.
When it is necessary to replace one belt in a given set,
the entire set of belts must be replaced.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE – YEARLY
Check the fan wheels and inspect the drain pan for
sludge and foreign material. Clean if required.
Observe the operation of all dampers and make any
necessary adjustments in linkage and blade orientation
for proper operation.
Entire Unit Inspection
In addition to the checks listed in this section, periodic
overall inspections of the unit should be accomplished
to ensure proper equipment operation. Items such as
loose hardware, component operation, refrigerant
leaks, unusual noises, etc. should be investigated and
corrected immediately.
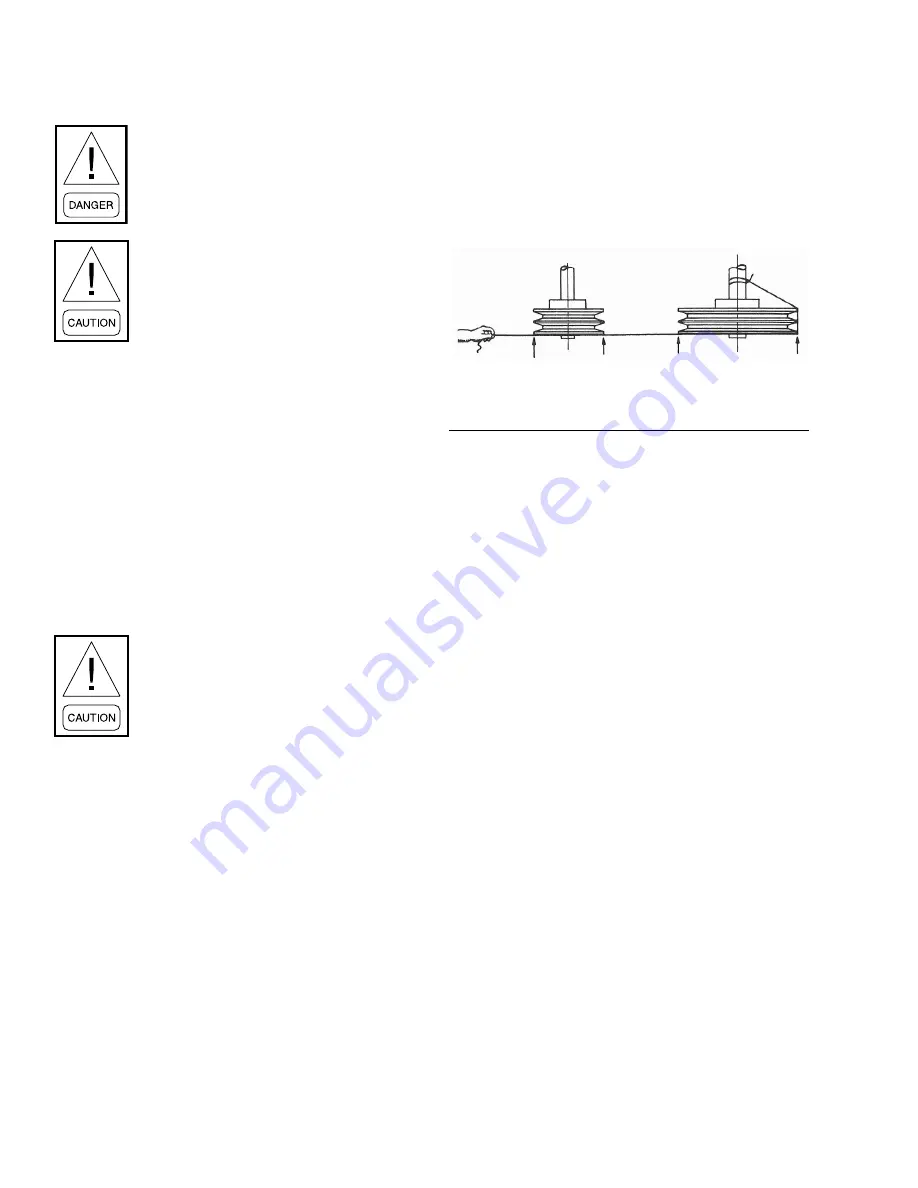
FIGURE 23 -
SHEAVE ALIGNMENT
LD07634
CORD TOUCHING SHEAVES AT
POINTS INDICATED BY ARROWS
CORD TIED
TO SHAFT
Sheave Alignment
To check sheave alignment, a straight edge or a piece of
string can be used. If the sheaves are properly aligned,
the string or straight edge will touch at all points, as
indicated in
. Rotating the
sheaves will determine if the sheave is wobbly or the
drive shaft is bent. Alignment error must be corrected
to avoid bearing and belt failure.
Belts
New belts should be re-checked after 24 hours of op-
eration. On multiple belt adjustable pulleys, the pitch
depth should be checked to insure identical belt travel,
power transfer and wear. Adjustable motor bases are
provided for belt adjustment.
Motor pulleys and blower shaft pulleys are locked
in position with either set screws or split taper lock
bushings. All set screws and/or taper lock bolts must
be checked for tightness and alignment before putting
equipment into operation.
An incorrectly aligned and tensioned belt can substan-
tially shorten belt life or overload blower and motor
bearings, shortening their life expectancy. A belt ten-
sioned too tightly can overload the motor electrical,
causing nuisance tripping of the motor overloads and/
or motor failure and/or shaft failure.
















































