Page 14
Operation and Maintenance Instructions
Envistar Top 04-21
DSET.181201.00.EN
Continuous product development may give rise to specification changes without notice.
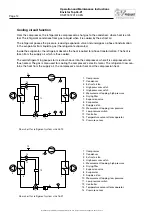
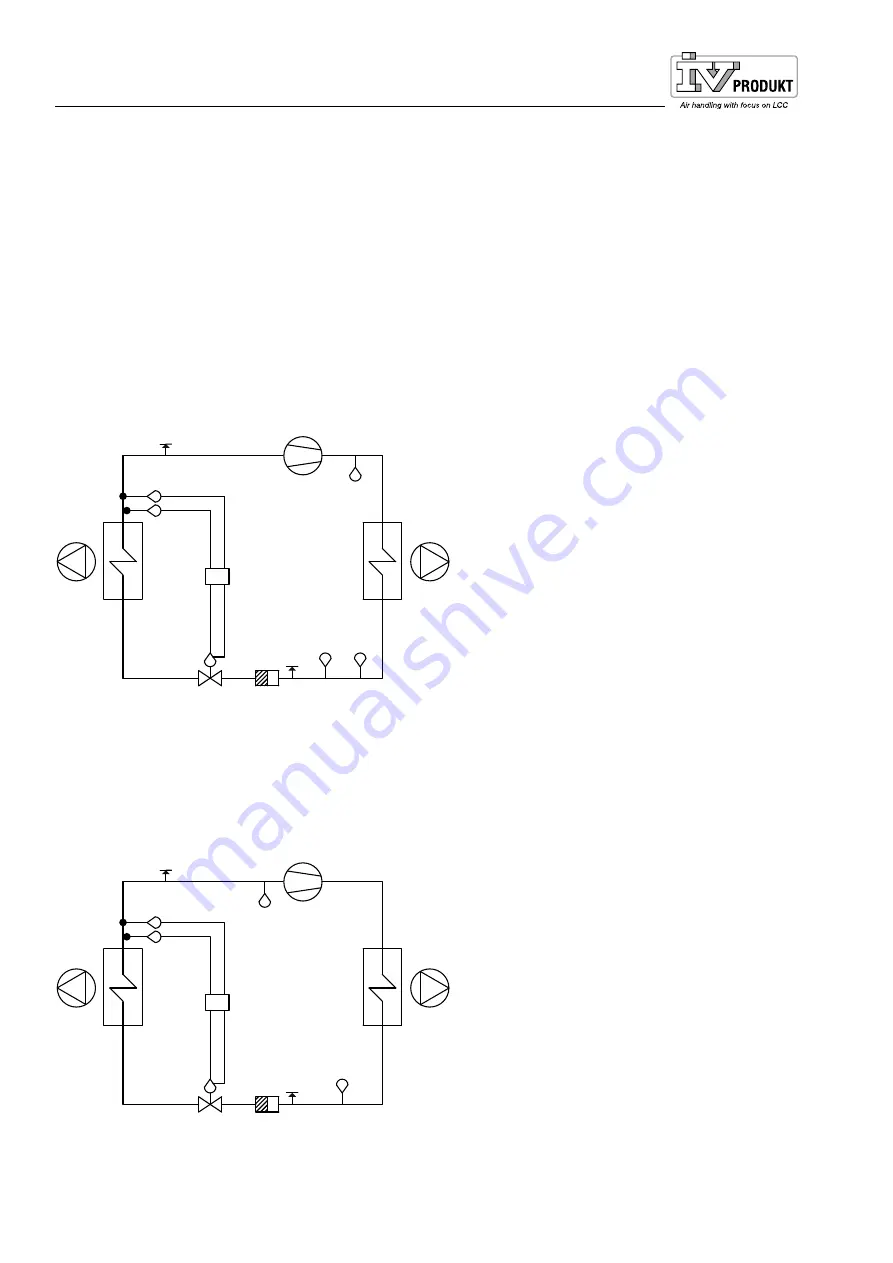
Cooling circuit function
From the compressor, the refrigerant is compressed as hot gas to the condenser, where heat is emit-
ted. The refrigerant condenses from gas to liquid when it is cooled by the extract air.
The refrigerant passes the pressure reducing expansion valve and undergoes a phase transformation
in the evaporator from liquid to gas (the refrigerant evaporates).
Inside the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs the heat required for phase transformation. The heat is
taken from the supply air which is thus cooled.
The cold refrigerant in gaseous form is drawn back into the compressor, where it is compressed and
thus heated. The gas is also used for cooling the compressor’s electric motor. The refrigerant now con-
tains the heat from the supply air, the compressor’s motor heat and the compression heat.
15
13
14
10
4
11
2
12
5
6
1
9
7
8
3
1 Compressor
2 Condensor
3 Extract air fan
4 High pressure switch
4 High pressure switch
5 Measurement tapping, high pressure
6 Drying filter
7 Expansion valve
8 Evaporator
9 Supply air fan
10 Measurement tapping, low pressure
11 Low pressure switch
12 Controller
13 Temperature sensor after evaporator
14 Pressure sensor
Flow chart for refrigerant system size 04-12
14
12
13
8
3
9
11
10
4
1
7
5
6
2
1 Compressor
2 Condensor
3 Extract air fan
4 High pressure switch
5 Measurement tapping, high pressure
6 Drying filter
7 Expansion valve
8 Evaporator
9 Supply air fan
10 Measurement tapping, low pressure
11 Low pressure switch
12 Controller
13 Temperature sensor after evaporator
14 Pressure sensor
Flow chart for refrigerant system size 16
-
21