2
July 6, 2010
AN1559.0
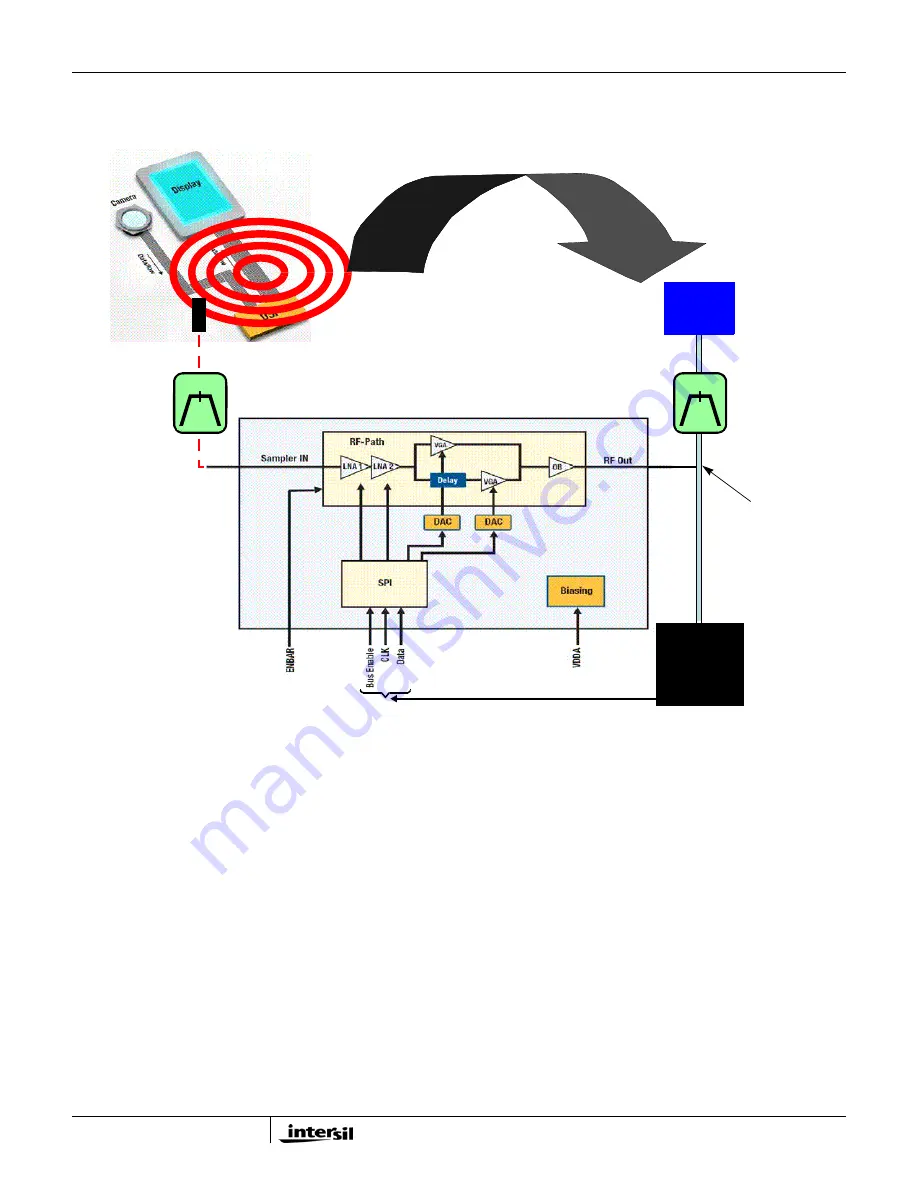
QHx220 System Overview
General Application System Block Diagram for QHx220
Description of QHx220 System Block
Diagram
The block diagram shown in Figure 1 illustrates the
typical system architecture for the implementation of the
QHx220 noise canceller. The QHx220 integrates the LNA
gain stages in the sampler path as well as the DACs
which control the I and Q (or ultimately the gain and
phase) of the device. The LNA gain stages and the I and
Q are controlled via the SPI bus interface. The GUI
software supplied with the evaluation board provides a
means to manually tune all of these parameters.
A known noise source is sampled by a variety of tapping
methods depending on the accessibility of sampling the
noise source. The sampled noise is then filtered by a
bandpass filter that has the same bandwidth as the
victim receive band. It may be possible to eliminate this
filter stage. However, this is dependent on the
characteristics of the aggressor source, the sampling
methodology and the location of the cancellation node
within the receiver chain. The QHx220 has internal LNA
gain stages that can be set to pre-amplify the sampled
input noise if necessary. The amount of pre-amplification
required (if any) depends on coupling factors between
the noise source and the victim antenna as well as the
level of the sampled noise at the input of the QHx220.
Since the dynamic range of the QHx220 is typically 50dB,
the noise level at the input of the QHx220 should be
approximately 25dB higher than the noise level present
at the victim receiver (when using the minimum gain
setting). Higher gain settings should be used when it is
not possible to find a strong enough tapping point of the
noise source. Setting this level correctly will allow for a
maximum tuning range when using the QHx220 tuning
control. This characterization will determine the amount
of pre-amplification necessary for any given application.
It is important to remember not to exceed the -45dBm
maximum input power of the QHx220 device. The
QHx220 has a high output impedance which only
introduces, on the order of tenths of a dB, insertion loss
FIGURE 1. TYPICAL APPLICATION DIAGRAM
SAMPLER
CANCELLATION
NODE
COUPLING CHANNEL
VICTIM
ANTENNA
NOISE SOURCE
SIGNAL INTEGRITY
VIA SPI BUS
VICTIM
RECEIVER
AND
BASEBAND
PARAMETER FEEDBACK
F
C
F
C
QHx220
Application Note 1559


































