4
3.0 POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
3.1
Complications Associated with Implantation
As with any surgical procedure, the implantation of the
OPTIMIZER Smart Mini IPG involves some degree of risk. This
section is intended to provide you with an explanation of the
various potential complications associated with having a device
implanted. These potential complications are not unique to the
OPTIMIZER Smart Mini IPG, as they may also occur during the
implantation of other implantable cardiac devices (e.g., cardiac
pacemakers or defibrillators).
The risks associated with the implantation are listed in
Table 1
and are grouped based on their prevalence.
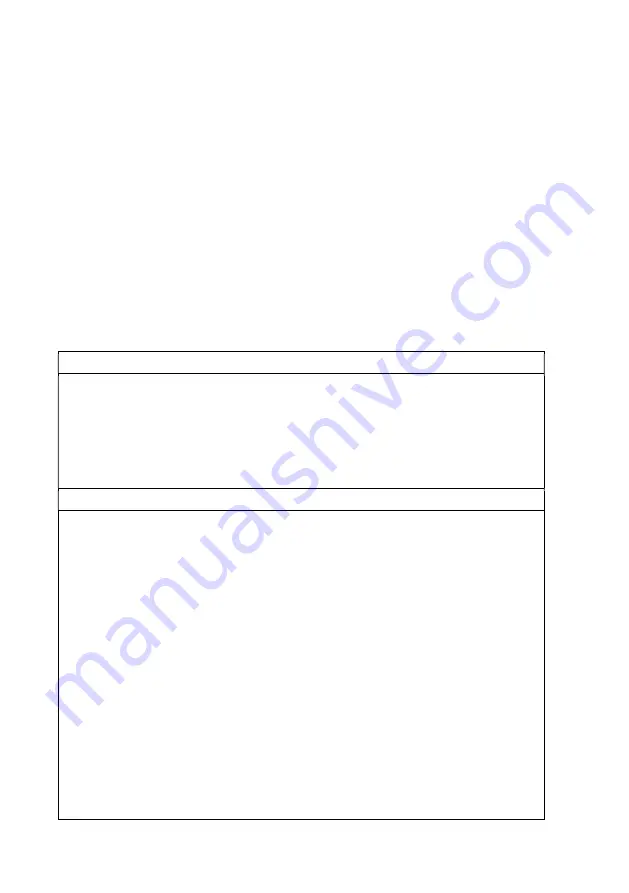
Table 1: Risks Associated with Implantation
Common (greater than or equal to 5%)
Post-procedural pain, bruising, and discomfort at insertion site
Bleeding
Infection at site of insertion
Pocket hematoma
Migration of leads
Migration of implanted IPG
Uncommon (between 1-5%)
Chest trauma (such as a collapsed lung or bleeding into the
chest)
Generator complication
Cardiac perforation (puncture of the heart caused by the
leads)
Endocarditis (infection of the heart valves)
Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat, including heartbeats that are
too slow or too fast)
Tricuspid valve damage (the valve between the right upper
and lower chambers of the heart that prevents blood from
flowing back into the upper chamber), possibly leading to
tricuspid valve regurgitation or leakage
Vessel trauma (perforation, dissection, or rupture)
Thrombosis (formation of blood clots in the veins)
Damage to the specific type of heart tissue responsible for
triggering heartbeats (i.e., the cardiac conduction system)
Allergic reaction











































