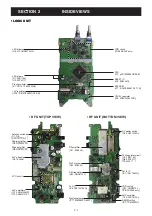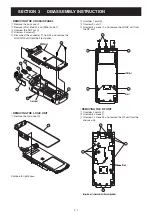
4 - 2
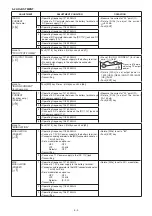
R5
R5
AM AF signal
to the AM/FM
switch (IC2, pin 6)
FM AF signal to the
AM/FM switch (IC2, pin7)
IC2 TA31136F
1st IF (30.05 MHz) from
the IF amplifier (Q13)
Q18
C111
R92
R95
C108
Q17
R97
R96
R94
C112
C109
D40
Q16
AM
FM
Q15
R89
R86
R91
R87
C101
C104
C103
D41
FI2
2nd IF filter
450 kHz
3
Mixer
2
(29.6 MHz)
14
PLL IC
IC3
5
X2
29.6 MHz
16
IF amp.
detector
FM
11
9
10
C91
C201
X1
R5
R71
R72
R73 R274
C95
C93
C92
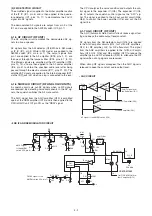
AF signal to the AM/FM switch (IC2)
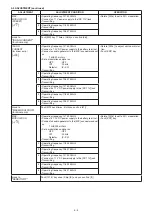
AGC
AMP
AGC
AMP
AMP
2nd lF
AMP
2nd lF
AMP
2nd lF
AM
DET
Q18
Q17
Q16
Q15
2nd IF signal from
the 2nd mixer (IC1)
Q14
Q10
to the 1st IF amplifier (Q13)
to the RF amplifier (Q11)
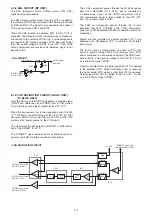
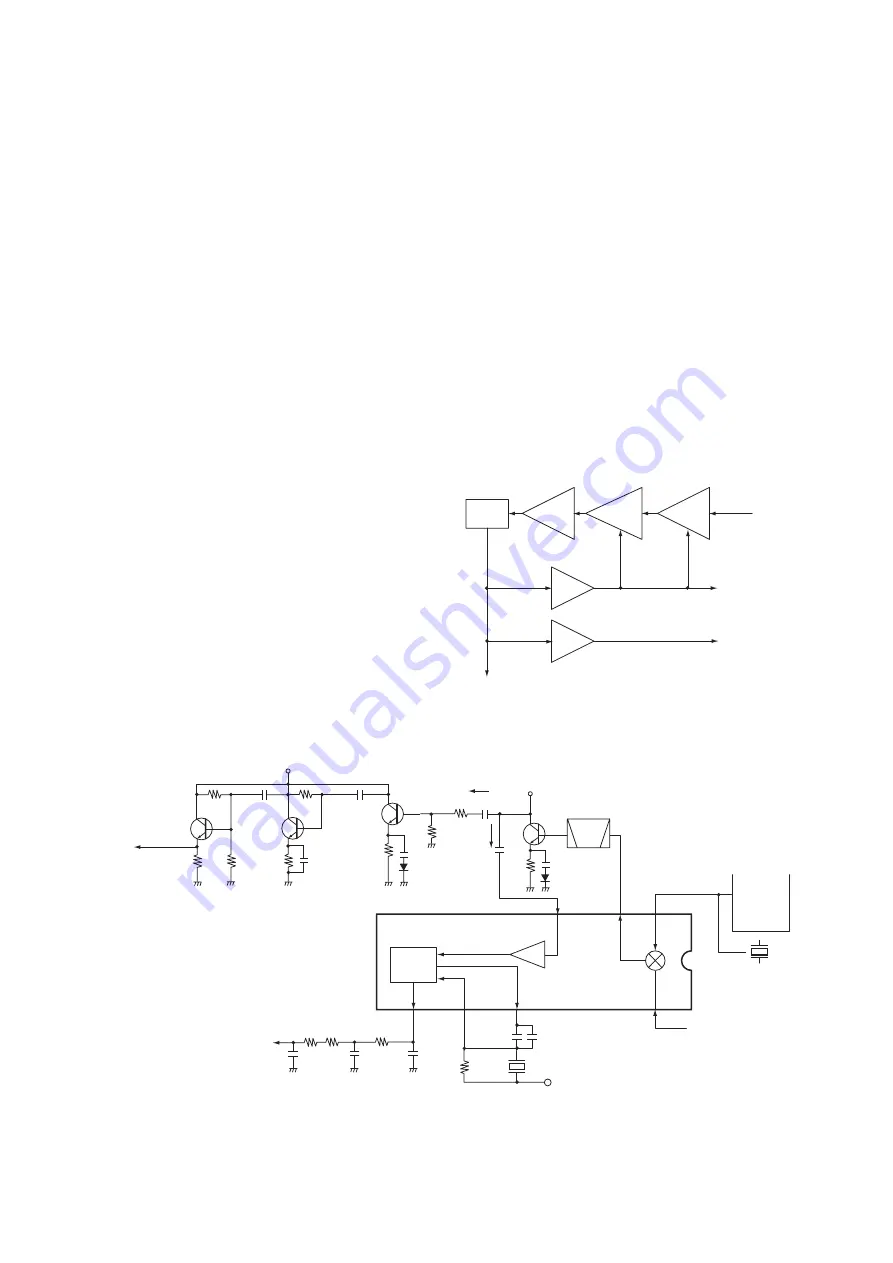
• 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUIT
• AGC CIRCUIT
(2) FM DETECTOR CIRCUIT
The amplified signal is applied to the limiter amplifier section
of the IF IC (IC1, pin 5) and is then applied to the quadra-
ture detector (IC1, pins 10, 11) to demodulate the 2nd IF
signal into AF signals.
The demodulated AF signals are output from pin 9 of the
IC1 and are applied to the AM/FM switch (IC2, pin 7).
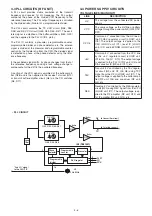
4-1-5 AF CIRCUIT (RF UNIT)
The AF amplifier circuit amplifies the demodulated AF sig-
nals to drive a speaker.
AF signals from the AM detector (Q18; While in AM mode)
or IF IC (IC1, pin 9; While in FM mode) are applied to the
AM/FM switch (IC2, pin 6 or 7). The output signals from
pin 1 are applied to the AF amplifier (IC18, pins 1, 2), and
then pass through the low-pass filter (IC18, pins 5, 7, 8, 10).
The filtered signals are amplified at the OP-amplifier (IC18,
pins 13, 14), and are then applied to the AF power amplifier
(IC6, pin 4) to obtain the specified audio level after being
passed through the electric volume (IC17, pins 21, 22). The
amplified AF signals are applied to the internal speaker (SP1)
via the [SP] jack (J5) when no plug is connected to the jack.
4-1-6 SQUELCH CIRCUIT (RF AND LOGIC UNITS)
A squelch circuit cuts out AF signals when no RF signals
are received. By detecting noise components in the AF sig-
nals, the squelch switches the AF mute switch.
The AGC signal from the AGC amplifier (Q10) is amplified
again at the RSSI amplifier (IC13) and is then applied to the
CPU (LOGIC unit; IC1,pin 29) as the “RSSI” signal.
The CPU analyzes the noise condition and outputs the con-
trol signal to the expander IC (IC5). The expander IC (IC5,
pin 4) outputs the squelch control signal as the “AFC” sig-
nal. The signal is applied to the AF out control circuit (Q36,
Q35) to control the power amplifier (IC6) and cut the AF
signal line.
4-1-7 AGC CIRCUIT (RF UNIT)
The AGC (Automatic Gain Control) circuit reduce signal fad-
ing and keeps the audio output level constant.
AF signals from the AM detector circuit (Q18) are applied
to the AGC amplifier circuits (Q14; for 1st/2nd IF amplifiers,
Q10; for RF amplifier, Q9; for RF attenuator). The signal
from the AGC amplifiers is applied to the 1st/2nd IF ampli-
fiers (Q13, Q15, Q16) and RF amplifier (Q11) to reduce the
amplifier gain and RF attenuator (D29) to attenuate the RF
signals when strong signals are received.
When strong RF signals disappear, then the AGC signal is
released to keep the constant audio output level.