17 / 51
Non-hazardous-duty version
Power supply
Nominal voltage
24 V DC
Maximum voltage (U
input
):
35 V DC
Minimum voltage (U
input
):
dependent on load impedance, see graph below
Load impedance R
A
Loop resistance, R
loop
R
HART
+ R
cable
+ R
ammeter
Ohm
Minimum load impedance R
A
0 Ohm
Maximum load impedance R
A
750 Ohm
R
HART
resistance for HART® communication
250 Ohm, recommended
Line A = minimum voltage at the VF04 2-wire terminals
Line B = minimum supply voltage (for voltage drop caused by a 250 Ohm loop resistance)
Example for calculating the power supply: The voltage drop is tested at 22 mA:
U
power minimum 22
= 22 mA x load imp U
input minimum 22
U
power minimum 22
= 22 mA x 250 Ohm + 10 V = 5.5 V + 10 V = 15.5 V
In order to cover the whole current range, the voltage drop must also be tested at 4 mA:
At 4mA: U
power minimum 4
= 4 mA x load imp U
input minimum 4
U
power minimum 4
= 4 mA x 250 Ohm + 18 V = 1 V + 18 V = 19 V
At a load impedance of 250 Ohm a power supply voltage of 19 V is sufficient to energize the current device range of 4 to 20 mA.
Hazardous-duty version (Refer to pg. 50 for ATEX Safety Guidelines.)
Connect the wires of the current loop to terminals 2 and 3 (any polarity).
The intrinsically safe certified device may only be used in conjunction with another intrinsically safe certified equipment.
All the allowed electrical safety data indicated on the nameplate must be observed.
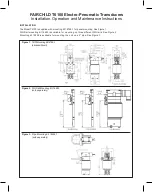
=
U
S
R
A
HART
4 ... 20mA
U
E
mA
L
VF04
Loop current, mA
V
o
lt
a
g
e
,
V
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Voltage drop
over 250
resistance at
4 mA
Ω
Minimum input voltage V
(measured at VF04 terminals)
input
Voltage drop
over 250
resistance at
20 mA
Ω
Minimum
y
,V
, , for a loop
resistance, R
of
(measured at
the terminals of the power supply)
suppl voltage
supply
loop
250
Ω