Some errors involving one or more updaters might require you to resynchronize certain files;
see the EMS event log for further information. Any error that cannot be explained should be
reported to your service provider.
For information about the causes, effects, and recovery actions for all RDF event messages, see
Appendix C (page 365)
or at the RDFCOM prompt enter the HELP command followed by the
RDF event number. For example, to see the Cause, Effect, and Recovery text for RDF event 895,
enter the following to the RDFCOM prompt:
] HELP 892
When present, file-system error numbers appear in the
error#
attribute of these messages.
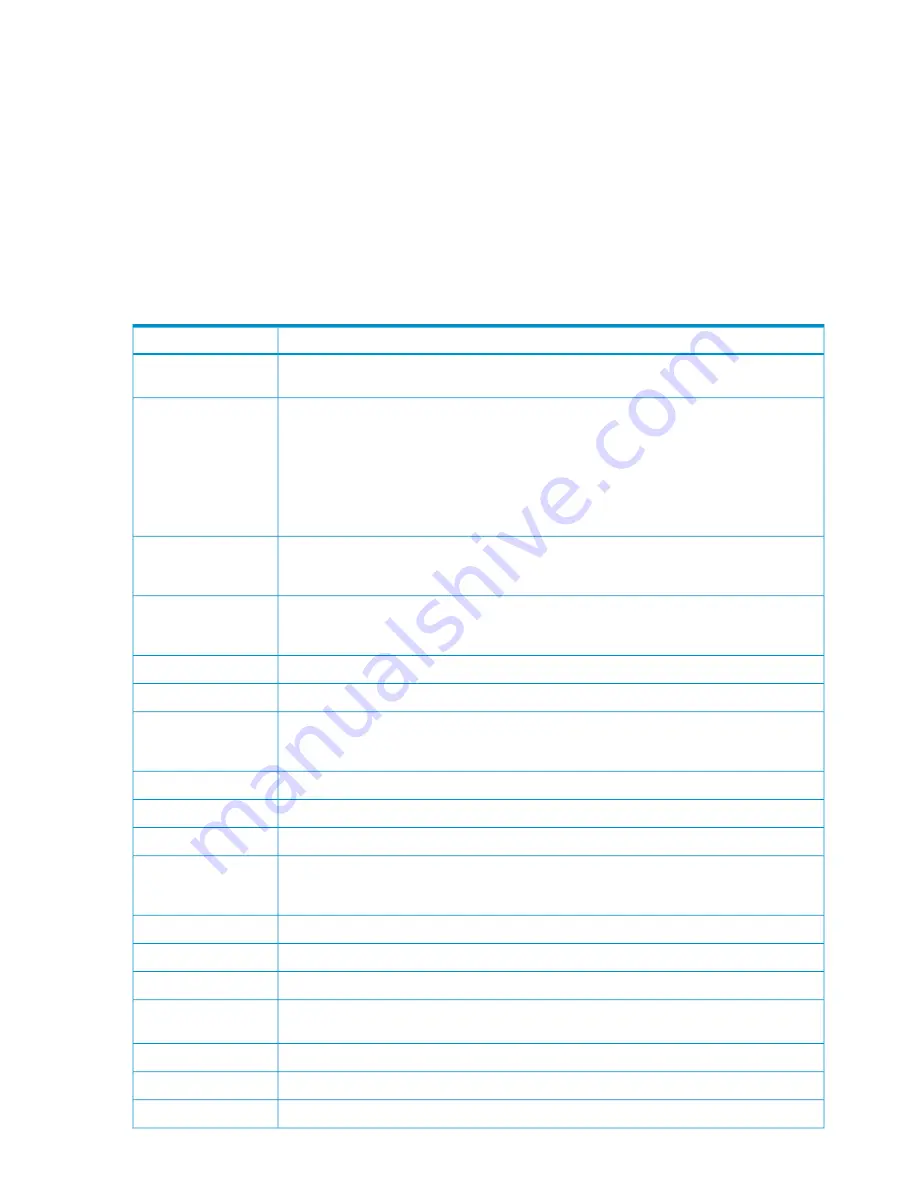
Table 5-1
lists the file-system error numbers and recovery actions for RDF event 700, which
reports file-modification failures.
Table 5-1 Recovery From File Modification Failures (RDF Event 700)
Recovery Action
File System Error
Check file integrity. The updater process skips the modify operation. RDF reports error 1
if an updater receives a “record not found” error while attempting to perform the operation.
1
An invalid operation occurred. An error 2 can be caused by a variety of reasons. For example,
error 2 is returned if an application has a data file open for shared write access and an
updater then attempts to open that same file for exclusive write access. This is a critical
error. You should stop RDF and investigate. If you cannot determine the cause of the error
and remedy the situation, contact your service provider. If an updater reports an error 2
while attempting to apply an audit record, it skips that record and goes to the next. In this
case, after you correct the error condition, you must reinitialize and reconfigure RDF to a
point earlier than the record that caused the error, and then restart RDF.
2
Check the file integrity. This could mean either loss of data or duplicated audit records. If
data was lost, resynchronize the file. If audit records were duplicated, then no harm occurred.
The updater process skips the modify operation.
10
Check the file integrity. This could mean either loss of data or duplicated audit records. If
data was lost, resynchronize the file. If audit records were duplicated, then no harm occurred.
The updater process skips the modify operation.
11
Check file integrity.
16
If the problem persists, alter hardware configuration or perform system tuning.
30 through 37
Provide more room for the file or extent by using FUP commands, such as PURGE and
ALTER MAXEXTENTS, or by compressing files. You might need to issue a STOP UPDATE
command.
43 through 45
Repair the device or clear the condition.
50 through 58
Check file integrity.
59
Repair the device or clear the condition.
60 through 66
Check the file integrity. This could mean either loss of data or duplicated audit records. If
data was lost, resynchronize the file. If audit records were duplicated, then no harm occurred.
The updater process skips the modify operation.
71
Repair the device or clear the condition.
100
Repair the device or clear the condition.
103
Repair the device or clear the condition.
120 through 121
Repair the device or clear the condition. An error 122 or 211 indicates the loss of the primary
CPU of a disk process. This is a normal error from which the RDF process will recover.
122, 211
Repair the device or clear the condition.
130 through 139
Check file integrity.
157
Repair the device or clear the condition.
190
122
Critical Operations, Special Situations, and Error Conditions
Summary of Contents for NonStop RDF
Page 68: ...68 ...
Page 186: ...186 ...
Page 260: ...260 ...
Page 278: ...278 ...
Page 284: ...284 ...
Page 290: ...290 ...
Page 308: ...308 ...
Page 322: ...322 ...
Page 336: ...336 ...
Page 348: ...348 ...
Page 464: ...464 ...
Page 478: ......
















































