189
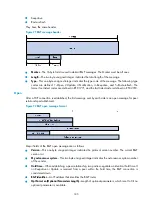
Use the AS_PATH attribute for route selection and filtering. BGP gives priority to the route with the
shortest AS_PATH length, if other factors are the same. As shown in
, the BGP router in
AS 50 gives priority to the route passing AS 40 for sending data to the destination 8.0.0.0.
In some applications, you can apply a routing policy to control BGP route selection by modifying
the AS_PATH length.
By configuring an AS path filtering list, you can filter routes based on AS numbers contained in the
AS_PATH attribute.
•
NEXT_HOP
Different from IGP, the NEXT_HOP attribute may not be the IP address of a directly connected
router. It involves the following types of values, as shown in
{
When advertising a self-originated route to an EBGP peer, a BGP speaker sets the NEXT_HOP
for the route to the address of its sending interface.
{
When sending a received route to an EBGP peer, a BGP speaker sets the NEXT_HOP for the
route to the address of the sending interface.
{
When sending a route received from an EBGP peer to an IBGP peer, a BGP speaker does not
modify the NEXT_HOP attribute. If load-balancing is configured, the NEXT_HOP attribute of
the equal-cost routes is modified. For load-balancing information, see "
Figure 77
NEXT_HOP attribute
•
MED (MULTI_EXIT_DISC)
The MED attribute is exchanged between two neighboring ASs, each of which does not advertise
the attribute to any other AS.
Similar to metrics used by IGP, MED is used to determine the best route for traffic going into an AS.
When a BGP router obtains multiple routes to the same destination, but with different next hops, it
considers the route with the smallest MED value the best route given that other conditions are the
same. As shown in
, traffic from AS 10 to AS 20 travels through Router B that is selected
according to MED.