Function Blocks
Function Block Reference Guide
3/99
114
2.43 ONDT Function Block
Description
The
ONDT
label stands for the
On Delay Timer
.
This block is part of the
Fast Logic and Counters/Timers
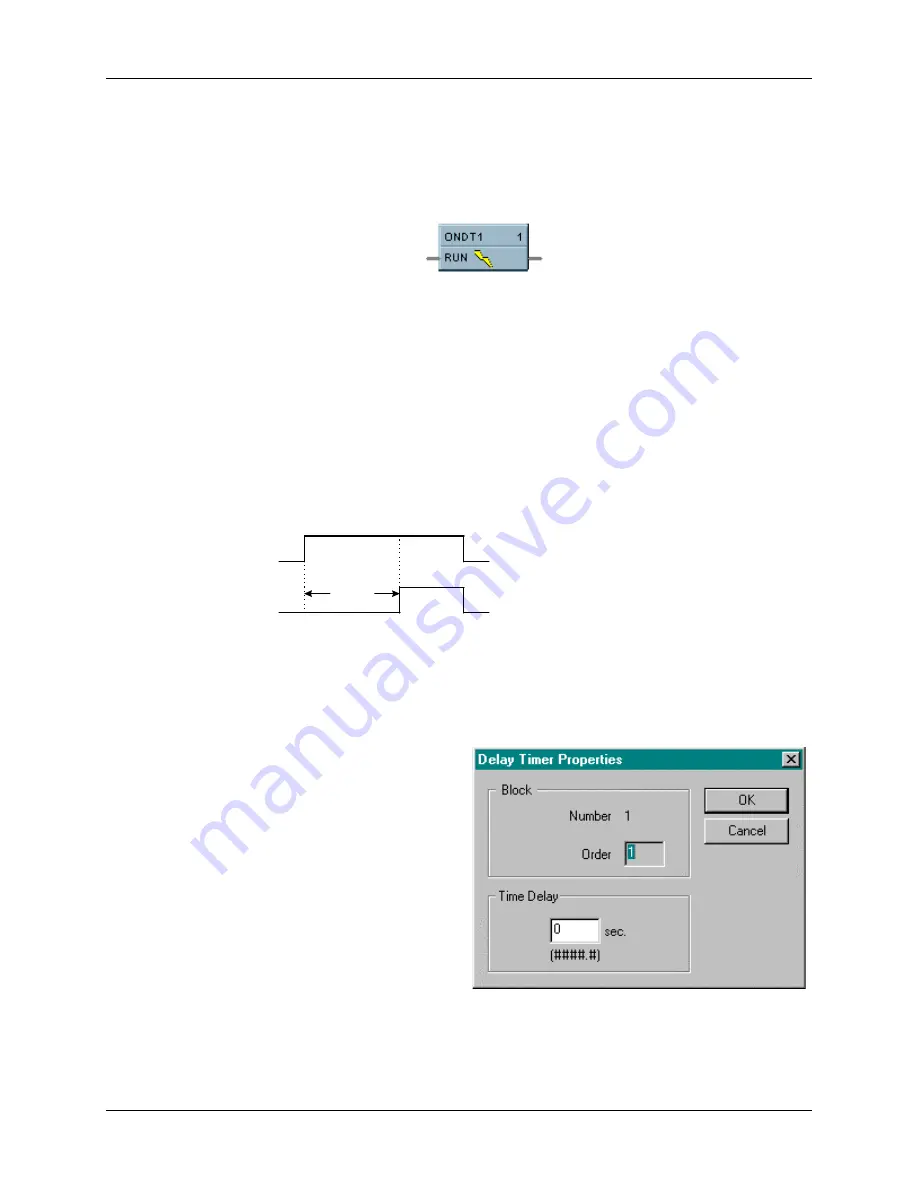
categories. It looks like this graphically on the Control Builder.
Function
Provides an ON state logic output delayed by a user specified delay time after an OFF to ON transition of
the RUN input.
An ON to OFF transition of the RUN input before the delay time has elapsed causes the timer to reset.
Transitions from OFF to ON of the input are not delayed.
•
If RUN is OFF, then OUT = OFF
•
If previous RUN input is OFF and RUN is ON, then TIMER = DELAY, else if timer is not zero,
then TIMER = TIMER -1.
•
If RUN is ON and TIMER is 0, then OUT = ON (delay time has timed out).
Timing Diagram
On Delay
1
0
1
0
Run
Input
Output
Input
RUN = Logic Input
Output
OUT = Logic Output
Block Properties
Double click on the function block to access the
function block properties dialog box.
Block Order (Read Only)
You can change the assigned execution order
number by selecting “Execution Order” in the
“Configure” menu and arrange the order to suit
your control strategy.
Configuration Parameters
You must configure the ONDT function Block
parameters to the desired value or selection that
matches your operating requirements.
describes the parameters and the
value or selection.
Continued next page
















































