OPERATION
HOLZMANN MASCHINEN GmbH www.holzmann-maschinen.at
37
BF16V
•
Recommendation: up cut milling during roughing and climb milling during finishing.
•
Remove clamped milling tools before cleaning the machine.
18.7.1
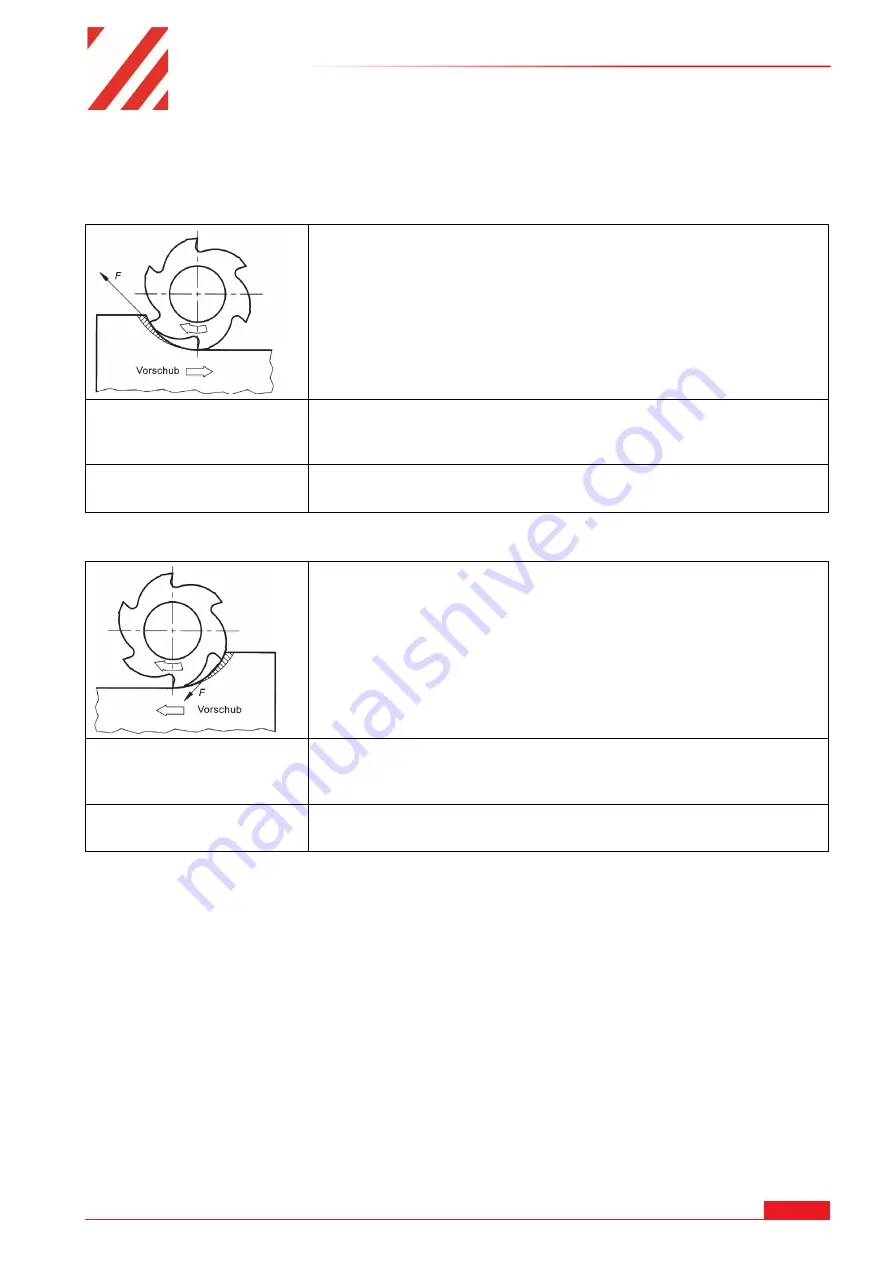
Up cut milling
In up-cut milling, the cutting direction of the milling cutter is
directed against the feed direction of the workpiece. Before the
milling cutter cutting edge penetrates the material, it slides over
the workpiece. This leads to increased wear. In accordance with
the chip formation, the cutting force F increases from zero to its
maximum. If the cutting edge leaves the material, the cutting
force drops abruptly. This leads to an undulating surface. Since the
cutting force counteracts the feed, any play in the feed drive has
no influence on the milling process.
Advantages:
•
Can be used on any machine.
•
Is particularly suitable for workpieces with hard surfaces, such
as a cast skin, weld seam or surface treatment.
Disadvantages:
•
A wavy surface is created.
•
High wear and tear and therefore short tool life time.
18.7.2
Climb milling
In climb milling, the cutting direction of the cutter points in the
same direction as the feed direction of the workpiece. The chip
cross section and the cutting force are greatest at the entry of the
cutting edge and then decrease steadily. This enables a high
surface quality. However, the sudden penetration of the cutting
edge into the workpiece can lead to a breakage of the cutting
edge on hard surfaces. The cutting force F acts in the feed
direction. This means that the workpiece can be pulled into the
milling cutter if there is play in the feed drive.
Advantages:
•
It can be worked with large cutting depht. Thus a high cutting
capacity is achieved.
•
A high surface quality is achieved (for finishing).
Disadvantages:
•
May only be used on machines with backlash-free feed drive.
•
May not be used on hard surfaces.
18.7.3
Milling tools
Milling tools, usually called cutters, are multi-bladed tools. State of the art high-alloy tool steels
(HSS) and hard metals are used to manufacture the milling cutters. In order to increase tool life
(operating time of the tool) and cutting performance, some of the milling cutters are still equipped
with a special surface coating. Milling tools are available in a wide variety of geometries, shapes
and types of entrainment (clamping). HSS milling cutters are divided into three tool types:
Type H (hard)
For high-strength and short-chipping materials (tool steel, CuZn (brass), ceramics, plastics such as
EP, PUR hard, UF and MF resins).
Type N (normal)
For materials up to 1000 N/mm
2
tensile strength (cast steel, malleable cast iron, stainless steels,
light metal alloys, plastics such as PS, PC, PMMA, )
Type W (soft)
For soft materials (copper, light metals zinc alloys, lead, plastics such as PVC, POM, PTFE, PE, PP).
















































