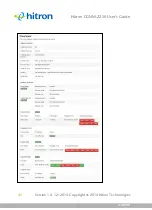
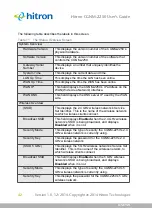
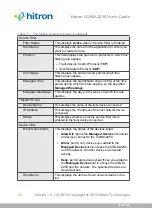
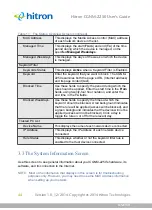
STATUS
Version 1.0, 12/2014. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
37
Version 1.0, 12/2014. Copyright 2014 Hitron Technologies
37
Hitron CGNM-2250 User’s Guide
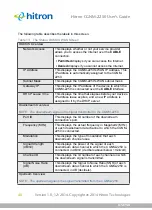
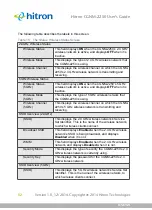
3.1.6
Routing Mode
When your CGNM-2250 is in routing mode, it acts as a gateway for computers on the
LAN to access the Internet. The service provider assigns an IP address to the
CGNM-2250 on the WAN, and all traffic for LAN computers is sent to that IP address.
The CGNM-2250 assigns private IP addresses to LAN computers (when DHCP is
active), and transmits the relevant traffic to each private IP address.
NOTE:
When DHCP is not active on the CGNM-2250 in routing mode, each
computer on the LAN must be assigned an IP address in the CGNM-2250’s
subnet manually.
When the CGNM-2250 is not in routing mode, the service provider assigns an IP
address to each computer connected to the CGNM-2250 directly. The CGNM-2250
does not perform any routing operations, and traffic flows between the computers and
the service provider.
Routing mode is not user-configurable; it is specified by the service provider in the
CGNM-2250’s configuration file.
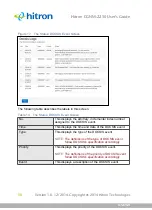
3.1.7
Configuration Files
The CGNM-2250’s configuration (or config) file is a document that the CGNM-2250
obtains automatically over the Internet from the service provider’s server, which
specifies the settings that the CGNM-2250 should use. It contains a variety of
settings that are not present in the user-configurable Graphical User Interface (GUI)
and can be specified only by the service provider.
3.1.8
Downstream and Upstream Transmissions
The terms “downstream” and “upstream” refer to data traffic flows, and indicate the
direction in which the traffic is traveling. “Downstream” refers to traffic from the
service provider to the CGNM-2250, and “upstream” refers to traffic from the CGNM-
2250 to the service provider.
3.1.9
Cable Frequencies
Just like radio transmissions, data transmissions over the cable network must exist
on different frequencies in order to avoid interference between signals.