SJ100 Inverter
xvii
Revisions
Revision History Table
No.
Revision Comments
Date of Issue
Operation
Manual No.
Initial release of manual NB585X
April 1999
NB585X
1
Revision A
Added 7.5 and 10 HP models to tables and drawings in
Chapt. 1 and 2,
Minor corrections throughout manual
May 1999
NB585XA
2
Revision B
Pages 1-4, 5 – Specs tables: corrected weights (lbs), added
row for input current, corrected dynamic braking % torque
Page 2-11 – Added note about fans at bottom of page
Page 2-15 – Added torque specs for 7.5 and 10 HP models
Page 3-36 – Added larger motor sizes to H_03/H203 motor
capacity settings in table
Page 3-41 – Added note about SLV operation at top of page
Pages 4-30, 31 – Changed text in notes for Steps 1, 2, and
10 in table to clarify auto-tuning procedure
Pages 4-31, 32 – Added auto-tuning notes at bottom of 4-31
and new page 4-32 about motor parameters, frame size, etc.
Page 5-5 – Added braking res. specs for 7.5/10 HP models
August 1999
NB585XB
3
Revision C
Updated company name on cover, contact page, and
nameplate photo
Updated text, figures, and tables throughout manual per
technical corrections or usability improvements
Pages xii to xiv – Added UL Instructions
Page xviii – Contact page update
Pages 1-5 to 1-8 – Added watt loss, efficiency data to tables
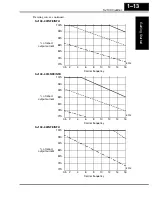
Pages 1-10 to 1-15 – Added derating graphs
Page 2-16 – Added power terminal diagrams
Page 4-5 – Added system wiring diagram
Page 4-7 – Added terminal index listing
Page 4-8 – Added input terminal wiring diagrams
Page 4-24 – Added output terminal wiring diagrams
Pages 5-5 to 5-10 – Added braking tables and figures
Page 6-10 – Added megger test procedure and figure
Page 6-15 – Added IGBT test method, figure, and table
Pages C-1 to C-6 – Added appendix on CE-EMC
Removed DOP+ info from Ch3 and Appendix B
May 2002
NB585XC
4
Revision D
Minor corrections throughout
Nov. 2002
NB585XD
5
Revision E
Minor corrections throughout
July 2003
NB585XE
5
Revision F
Minor corrections throughout
Dec. 2003
NB585XF