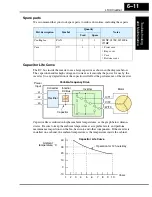
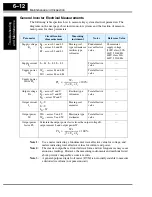
Maintenance and Inspection
T
roub
leshooting
and Maintenance
6–14
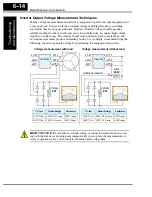
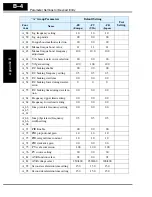
Inverter Output Voltage Measurement Techniques
Taking voltage measurements around drives equipment requires the right equipment and
a safe approach. You are working with high voltages and high-frequency switching
waveforms that are not pure sinusoids. Digital voltmeters will not usually produce
reliable readings for these waveforms. And, it is usually risky to connect high voltage
signals to oscilloscopes. The inverter output semiconductors have some leakage, and
no-load measurements produce misleading results. So, we highly recommend using the
following circuits to measure voltage for performing the equipment inspections.
HIGH VOLTAGE:
Be careful not to touch wiring or connector terminals when work-
ing with the inverters and taking measurements. Be sure to place the measurement cir-
cuitry components above in an insulated housing before using them.
220 k
Ω
2W
+
–
220 k
Ω
2W
+
–
Voltage measurement
with
load
Inverter
Voltage measurement
without
load
Additional resistor
Inverter
5 k
Ω
30W
V Class
Diode Bridge
Voltmeter
200V Class
600V 0.01A min.
300V range
400V Class
100V 0.1A min.
600V range
V Class
Diode Bridge
Voltmeter
200V Class
600V 0.01A min.
300V range
400V Class
100V 0.1A min.
600V range
L1/R
L2/S
L3/T
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
L1/R
L2/S
L3/T
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3