--- 15 ---
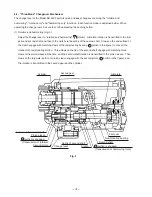
Second gear
Cylinder
Second shaft
Ring groove
Key rail (2 pcs.)
Clutch
Fig. 3
Piston
Piston pin
Reciprocating bearing
Armature
Tool shaft
Armature
shaft
Steel ball
Piston reciprocating mechanism
In conventional rotary hammers, a piston is caused to reciprocate by a connecting rod and crank shaft, and
the crank shaft and the cylinder axes are at right angle to each other. Accordingly, the armature shaft and the
cylinder axes are also at right angles to each other. In the Model DH 24PF, through adoption of a spiral drive
system (a mechanism using a reciprocating bearing), a more compact design has been achieved by arranging
the armature shaft in parallel with the cylinder axis. Referring to Fig. 3, the armature's rotation is transmitted
to the second shaft via the first gear. The second shaft's rotation is then transmitted through a spline to the
clutch, which engages with a reciprocating bearing and causes it to rotate. However, as illustrated, circular
grooves on the inner race of the reciprocating bearing are positioned on an angle of inclination with relation to
the second shaft. The rotation of the inner race and the shaft causes the angle of inclination to change
regularly forward and back with relation to the second shaft, and produces a rocking motion in the outer race
of the reciprocating bearing. Finally, a rod extending from the outer race of the reciprocating bearing is
connected to the piston by a piston pin, and causes the reciprocating motion of the piston.
First gear