26
ZonePRO
TM
needed on the PC and/or ZonePRO.
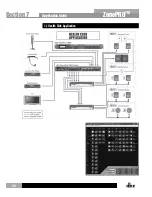
When networking two Ethernet capable devices without a hub or switch, an Ethernet crossover
cable must be used; the transmit and receive lines are crossed in an Ethernet crossover cable.
If connecting to a hub or switch, you will need to use Ethernet straight-through cables unless
your switch/hub supports auto MDI/MDIX.
6.3 Overview of TCP/IP Basics
Subnet
A small network within a larger network. For example, a TCP/IP network might be a subnet
of a venue’s network, which could include computers throughout the building, or a network
might be divided into subnets. For example, in a large installation, there may be one subnet
per rack or room.
IP address
An identifier for a computer or device on a TCP/IP network. Each device in a network has its
own IP address to identify it. Example: 126.126.17.42. Networks using the TCP/IP protocol
route messages based on the IP address of the destination. An IP address consists of four
numbers separated by periods. Each number can be zero to 255. The last number should not
be a zero or 255. For example, 126.126.17.1 could be an IP address. 126.126.17.0 would not
be a valid IP address.
Network ID and Host ID
A TCP/IP or IP address has two parts:
the NETWORK ID and the HOST ID. The NETWORK ID
identifies the network, and the HOST ID identifies either the subnet and device, or just the
device if there is no subnet.
The subnet mask is a code that indicates which part of the TCP/IP address is the NETWORK ID
and which part is the HOST ID. In subnet-mask code, 255 means “This part of the address is
the NETWORK ID”.
Example:
Suppose the IP ADDRESS of a device is 192.168.12.34 and the SUBNET
MASK is 255.255.0.0. That means, (192.168) is the NETWORK ID. The remaining set
of numbers (12.34) is the HOST ID. If your network stands alone (it is not part of
a larger network) then the HOST ID identifies each device in the network. If your
network is part of a venue’s larger network, your network is actually a sub-network or
subnet.
All devices in the network have the same network ID. There are many resources
available on the Internet for IP and subnet calculation.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
This is a protocol for automatically assigning IP addresses to devices on a network.
With dynamic (DHCP) addressing, a device might have a different IP address every
time it connects to the network. If a computer is NOT connected to a network with
a DHCP server, the computer will assign a default network ID into the TCP/IP address
and a default subnet mask. In this case the attached computer may need its IP address
Networking
Section 6