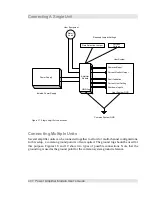
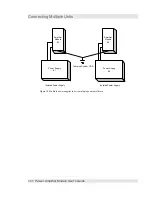
Electrical Connections
Description
Manufacturer
Supplier
Shorting Jumpers
3M/ISD
929950-00
Digi-Key
929950-ND
Selecting a Power Supply
A power supply is required to provide electrical power to the amplifier. The size, type and
capacity of the power supply are highly dependent on the application.
Operating Voltage
The operating voltage of the power supply should be chosen to match the power
requirements of the intended load. This will allow the amplifier to provide the maximum
power to the load while minimizing the power that is dissipated by the amplifier itself.
Proper selection of the operating voltage will allow the amplifier to remain cool, and
minimize the cooling requirements.
For a load resistance of 2 ohms, requiring a maximum current of 4A, Ohm's Law shows that
the required voltage is 8 Volts. Since the minimum operating voltage is 27 volts, this
voltage should be used.
v
=
iR
Similarly, the maximum current that the power amplifier can supply may be limited by the
supply voltage to the amplifier, even if the power supply can supply the current. For
example, if the load is 8 ohms, and the supply voltage is 27 volts, the maximum current is
given by:
i
=
v
R
which in this case results in a maximum current of 3A.
This shows the theoretical minimum voltage required, and in practice should be raised by at
least 3 volts, to account for the overhead required by the amplifier. In addition, if the power
supply is located a significant distance from the amplifier, drops in the supply voltage may
become critical. In this case the voltage of the power supply will need to be even higher.
38
Power Amplifier Module User's Guide