7
2.3 Hazards analysis and scenario Design Considerations setup
Fire is the output of three factors combination; a combustible product, ignition factor and
oxygen. VFDS™ system designer / installer must analyze the possible combustible materials
and possible resultant in the environment; also refer to fire case study to formulate the Fire
Scenario as a system design base.
Combustible material analysis
Investigate the possible combustible materials in the environment. The various classes of
combustibles are listed as below
Normal solid combustibles: Such as wooden products, fibers, wool textile, papers and
rubbers, which usually cause construction fire.
Liquid combustibles: Such as flammable fuel - petrol, gas, diesel, carbinol, methyl
alcohol, ethyl
;
or flammable gaseous matter - ethane and ethine
;
or flammable triolein -
such as paint materials, asphaltum, paraffin and ect.
Electrically energized equipment: Such as electronics equipments, power transformer,
cables, power panel and etc.
Flammable active metal: Such as magnesium, natrium, potassium and their alloy.
Ignition Sources factor analysis
Investigate possible ignition sources in the environment. Some possible ignition sources
are as follows
Energized electrical sources include short circuit, terminal melting, overload, bad
contact, heater, old harness and etc.
Mechanical factor: friction, strike, mechanism malfunction, boiler heat and etc.
Others: welding, static electronics, cigarette stub, arson, flashing lightening, chemical
reaction
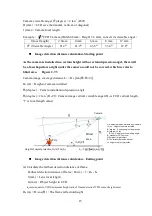
List the possible fire hazards as a consequence of your site survey, which shall consider the
issues raised above and take the worst case as the possible Fire Scenario. Usually VFDS™
system designers could take the fire properties of the fastest burning combustibles in the
environment and design the detection parameters based on this possible event.
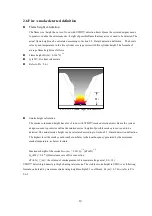
Different flammable materials have different fire properties including the fires growth rate
and Heat Release Rate. US NFPA defines different fire growth rates as Ultra-fast
、
Fast
、
Medium and Slow; so called as T-Squared Fires curve as Picture 2.3-1 illustrates. The
system designer is able to define the fire growth rate by choosing the combustibles reference
table as Pic. 2.3-1 and table 2.3-1. Process section 2.5 and 2.6 to calculate proper Heat