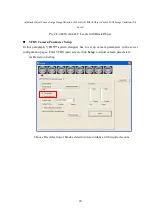
16
(H
f
is the actual flame height, and
θ
1
is the tilt depression angle of the camera.)
Note: The smallest flame VFDS can detect
Flame / height ratio=15/240=0.0625
(b) Calculate the farthest distance for smoke detection
The farthest distance for smoke detection: D
s
(m) = f
× H
s
/ h
s
f
(mm)
:
The lens focal length
h
s
(mm)
:
The object height in CCD image sensor
(=VFDS minimum smoke detection height ratio*CCD sensor height(mm))
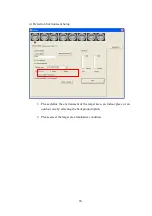
H
p
(m) = H
s
cos(
θ
1
)
:
Smoke reflection height. H
s
is the actual smoke height and
θ
1
is the tilt depression angle of the camera.
Note: VFDS smallest smoke VFDS can detect
Smoke detection / height ratio=30/240=0.125
After realizing above procedures, we can determine the farthest detection distance for
VFDS™ base on our protection purpose.
Case A-> Camera detects only flame: the farthest flame detection distance is D
f
.
Case B -> Camera detects only smoke: the farthest smoke detection distance is D
s
.
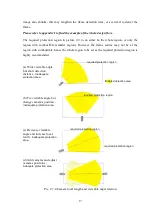
Case C -> Camera detects both flame and smoke:
The farthest detection distance for each camera will be the smaller value of either D
f
or
D
s
. According to the shortest and farthest detection distance, the detection area can be
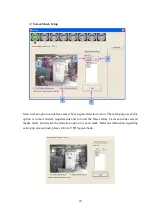
drawn out as sector shape. Please refer to the yellow region in picture 2.7-4(a).
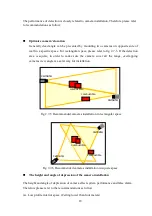
Camera position and quantity adjustment
After calculating the farthest detection distance and viewable angle, we could get the
sector-shaped maximum detection area, as shown in the yellow region in picture 2.7-4(a).
The system designer can change the position and direction of the cameras (which will change
the direction and starting point of the detection area). Check if this will cover the whole
required protection region, as shown in picture 2.7-4(b). If the whole area is covered, the
design is complete. Otherwise, either alter the camera focal length (recalculate the maximum
detection area) or add another camera to enlarge the coverage. Design is not finished until
the whole required protection area can be covered, as shown in 2.7-4(c) and (d). In general,
using smaller focal length lens (small f value lens) could cover wider detection area. Note
that when the focal length (f value) of the lens shrinks, the object forming in the VFDS™