5
263X Series Chlorine Electrodes
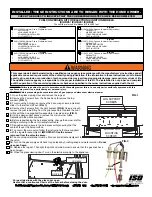
pH Compensation for Free Chlorine
Amperometric free chlorine sensors measure only hypochlorous
acid. As noted in the text above and in Figure 3, the ratio
of hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite is pH dependent. In
many applications the process pH is relatively stable and no
correction is needed. However, where the pH of the water
changes signi
fi
cantly, accurate free chlorine measurement
requires pH compensation. With the addition of a pH sensor, the
Signet 8630 transmitter will automatically compensate the free
chlorine reading for changes in pH.
5.0 5.5 6.0 6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5 9.0 9.5 10.0
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
HOCl
OCl
Ø
% free chlorine
pH at 25 °C
Chlorine Measurement by Amperometric Sensors
Signet chlorine sensors are membrane-covered amperometric 2-electrode sensors. A gold or platinum cathode acts as the working
electrode with a silver halide acting as the counter electrode. Depending on the species to be analyzed, a polarization voltage is
applied between the two electrodes. When placed into service, the chlorine species of interest diffuses across the membrane and
is reduced at the cathode surface. For the case of total chlorine, the analyte reacts with the
fi
ll solution to produce an intermediate,
which is subsequently reduced at the cathode surface. At the same time, the silver anode is oxidized to form a silver halide. The
current generated at the cathode is proportional to the rate of diffusion through the membrane and the concentration of chlorine in the
sample. The current from the cathode to the anode is conditioned, digitized and transmitted by the associated electronics.
9. Overview
Chlorine in Water
Various forms of chlorine are used to disinfect water. Each form of chlorine has bene
fi
ts and limitations which help determine the
speci
fi
c application. The predominant categories used in disinfection are Free Chlorine, Total Chlorine and Chlorine Dioxide. Free
Chlorine is the sum of chlorine gas (Cl
2
), hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite (OCl
-
). Above pH 4.0 all of the molecular
chlorine is converted to HOCl and OCl
-
. Hypochlorous acid is a more potent disinfectant than hypochlorite and exists in a pH
dependent equilibrium as shown in Figure 3.
Free chlorine also combines with naturally occurring or human-introduced nitrogen compounds in the water to form chloramines, also
known as combined chlorine. Treatment operators introduce ammonia into the water to form monochloramine (NH
2
Cl), dichloramine
(NHCl
2
) and trichloramine (NCl
3
). Chloramines are a less effective disinfectant but have a longer residence time than the free chlorine
species. Total chlorine is the sum of free chlorine (Cl
2
, HOCl and OCl
-
) and combined chlorine (NH
2
Cl, NHCl
2
, NCl
3
).
Mount the
fl
ow cell where the sensor will be easily accessible.
To avoid air bubble entrapment, do not mount with downward
fl
ow.
8. Mounting Position continued
Automatic pH Compensation and Free Chlorine
In many applications, the process pH does not signi
fi
cantly
fl
uctuate and only a chlorine sensor and instrument are
necessary for accurate chlorine measurement.
It is when the pH varies that free chlorine concentration can
not accurately be determined without the use of automatic pH
compensation.
The addition of the Signet 3-2724-00 (159 001 545) pH
electrode along with its 3-2750-7 (159 001 671) preampli
fi
er
to the system makes pH compensation extremely easy and
automatic even with wide
fl
uctuations or high pH.
See Figure 4 for pH variation recommendations.
Example
:
If the pH nominal value is 7.5 and the pH variation is ±0.2 then
automatic pH compensation is recommended.
If the pH nominal value is 7.0 and the pH variation is ±0.2 then
automatic pH compensation is not required.
6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 8.5 9.0
0
±0.3
±0.1
±0.2
=
pH variation
Sample pH
Automatic pH compensation recommended
in ranges within shaded area
NO
Flow
Figure 3
Figure 4