3
Electrical Connection
- continued -
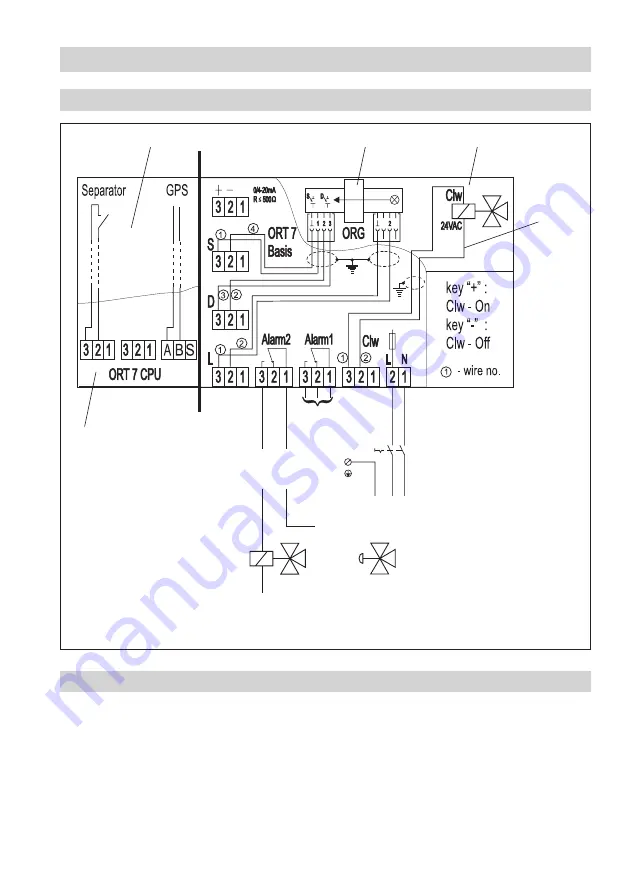
Wiring diagram OR 52-7
Fig. 4
Drawn position of contacts: Alarm 1 and 2, separator OFF and voltage failure
Notice
Fig. 4
shows an example where the water will be run back to the ship’s bilge in the event of an alarm
(oil content > 5 ppm) or auxiliary power failure.
With different limit settings alarm contact can, for instance, be used for the first alarm and alarm
contact 2 for the main alarm.
For bilge water monitoring a pneumatic three-way valve can be controlled by the alarm contact 2 via a
solenoid valve. If the turbidity of the effluent is too high (alarm caused by ingress of oil or dirt particles
introduced into the system during start-up) the three-way valve will divert the contaminated water to
the bilge tank. The separation continues until the oil content falls below 5 ppm and the cleaned water
can be discharged overboard.
External wiring
Measuring sensor
Disconnecting
switch
External
wiring
Purging valve
to first alarm
Attached in cover
Solenoid valve
Three-way valve
Earthing screw
in housing
PE L N
N
L
Summary of Contents for OR 52-7
Page 15: ...15 Functional Elements Measuring sensor ORG 12 Measuring transducer ORT 7 Fig 6 p n m o 9 e q ...
Page 32: ...32 Annex Type approval certificate ...
Page 33: ...33 Annex continued Type approval certificate continued ...
Page 34: ...34 Annex continued Type approval certificate continued ...
Page 35: ...35 Annex continued Type approval certificate continued ...
Page 36: ...36 Annex continued EC Prototype Test Certificate module B ...
Page 37: ...37 Annex continued EC Prototype Test Certificate module B continued ...
Page 38: ...38 Annex continued EC Type Examination Module B Certificate ...
Page 39: ...39 Annex continued EC Type Examination Module B Certificate continued ...
Page 40: ...40 Annex continued Declaration of Conformity ...
Page 41: ...41 For your notes ...
Page 42: ...42 For your notes ...
Page 43: ...43 For your notes ...














































