9
the linkage to rise until the prop (11, view D) can slip under
the close roller (10, view D) and hold the linkage in place. As
the linkage moves, the output crank (12, view D) rotates the
cross shaft (13, view D) which in turn rotates the phase bell
cranks and compresses the two opening springs (15, view E)
on poles 1 and 3, this closes the vacuum interrupters, and
compresses the three wipe springs (16, view E) on each pole.
The rotation of the cross shaft (13, view D) also changes the
auxiliary switch (7, view D) position. The position flag on the
front panel will then indicate “CLOSED”. After the breaker is
closed, the charging motor is again energized and the closing
spring is charged as described under “CLOSE SPRING
CHARGING”. Spring charging is possible when the breaker is
in the closed position because the linkage is held in place by
the prop.
5.4—Opening Operation (refer to Figure 15)
By either energizing the trip solenoid or depressing the
manual trip button (23, view B), the trip latch (19, view D) is
rotated, permitting the linkage to collapse and the vacuum
interrupter contacts to open under the force of the wipe
springs (16, view E) and opening springs (15, view E). At the
end of the opening stroke, the center phase wipe spring
assembly hits a stop block on the frame that limits overtravel
and rebound. Rotation of the cross shaft from the closed to
the open position operates the auxiliary switch (17, view D)
which opens the trip coil circuit. If the closing spring has been
recharged, the linkage will be reset and the trip latch will be in
place on the trip roller, ready for another closing operation.
5.5—Trip-free Operation
The linkage is mechanically trip free in any location on the
closing stroke. Electrically energizing the trip coil while closing
will, after the auxiliary switch contacts change position, rotate
the trip latch and permit the circuit breaker to open fully.
The linkage will reset as in a normal open operation, and the
closing spring will recharge as described under SPRING
CHARGING.
SECTION 6—Electric Control circuit
A typical PowerVac
®
circuit breaker ML-20 mechanism wiring
diagram is shown in Figure 16. Check the wiring diagram
supplied with the actual circuit breaker for its wiring.
The close spring-charging motor circuit is established through
the CL/MS (close latch monitor switch) switch if the close
latch is reset the SM/LS (spring motor limit switch) if the
closing spring is discharged and the IL/MS (Negative Interlock
Monitoring Switch). When the closing spring is charged, the
SM/LS interrupts the circuit.
The close coil circuit is established through two normally
closed 52Y relay contacts, and the latch-checking switch LCS,
if the trip latch is reset. An auxiliary switch contact 52b is also
in series with the close coil and closes when the breaker is
open and opens when the breaker is closed. During a close
operation, cam rotation closes the SM/LS contact allowing the
52Y relay to be energized; opening its contacts in the close
coil circuit and sealing itself in through one of its own contacts
to the close signal. This seal-in action prevents re-closing on a
sustained close command as the close signal must be
removed to drop out the Y relay, and reestablish the close
circuit, thereby providing an anti-pump feature.
Circuit breaker mounted auxiliary switch contacts not used in
the control circuit are bought out for control and indication
functions. The metalclad equipment may provide a breaker
operated stationary auxiliary switch for additional contacts
(3, 6 or 10 stages are available).
SECTION 7—Mechanical Checking and Slow Closing
7.1—Visual Inspection
Visually inspect the circuit breaker for any signs of damage or
loose hardware.
7.2—Closing Spring Charging
Manually charge the breaker closing spring using the charging
handle provided (1, Figure 4). The closing spring is charged by
a ratcheting mechanism that advances by one ratchet tooth at
a time. When the spring is fully charged and the spring load is
held by the closing latch, the spring indicator (3, Figure 1) will
change from “DISCHGD” to “CHARGED”, and a positive snap
will be heard as the spring travels over center.
CAUTION:
AFTER THE SPRING IS COMPLETELY
CHARGED, AS INDICATED IN FIGURE 4, FURTHER FORCING
CHARGING HANDLE MAY CAUSE DAMAGE TO THE
CLOSING LATCH AND ITS ASSOCIATED PARTS.
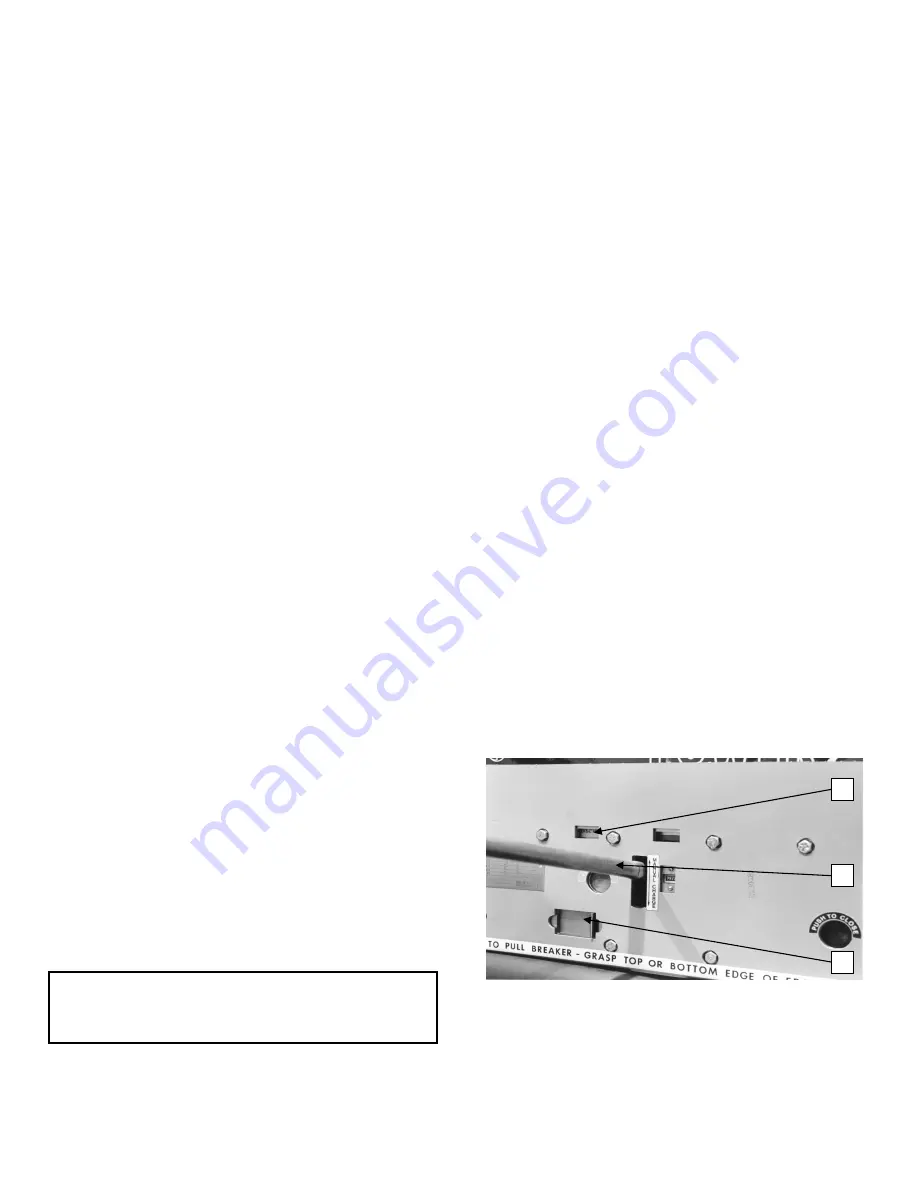
Figure 4 Manual charging
1. Manual charging handle
2. Close spring gag hole
(shown in closed position)
3. Spring charge indication
3
1
2
Summary of Contents for PowerVac
Page 1: ...DEH 40368 Instructions g PowerVac Vacuum Circuit Breaker with ML 20 Mechanism ...
Page 13: ...13 Figure 10 Control switches LCS Switch ...
Page 26: ...26 Figure 14 Continued C Breaker closed spring discharged D Breaker closed spring charged ...
Page 29: ...29 Figure 16 Typical wiring diagram for ML 20 mechanism ...
Page 39: ...Intentionally Left Blank ...