C-2
MIB High Impedance Bus Differntial Relay
GEK-106426A
C.2 DIGITAL FILTER
APPENDIX C
C
C.2DIGITAL FILTER
The first operation performed by the CPU with the voltage and/or current signal samples is the DFT.
The Discrete Fourier Transformation consists in decomposing a signal into a series of sinusoidal signals with frequencies
that are multiples of the fundamental frequency. If after this operation, we take the fundamental frequency signal, and we
disregard the rest of signals (harmonics), we will get a harmonic filter. This action is performed by the MIGII relay.
MIB uses a complete cycle recursive DFT, that is, for each sample it calculates the phasor from the previous sample
phasor and the difference between the current sample and the previous cycle sample. This makes the relay require a
complete cycle to obtain the correct measure value.
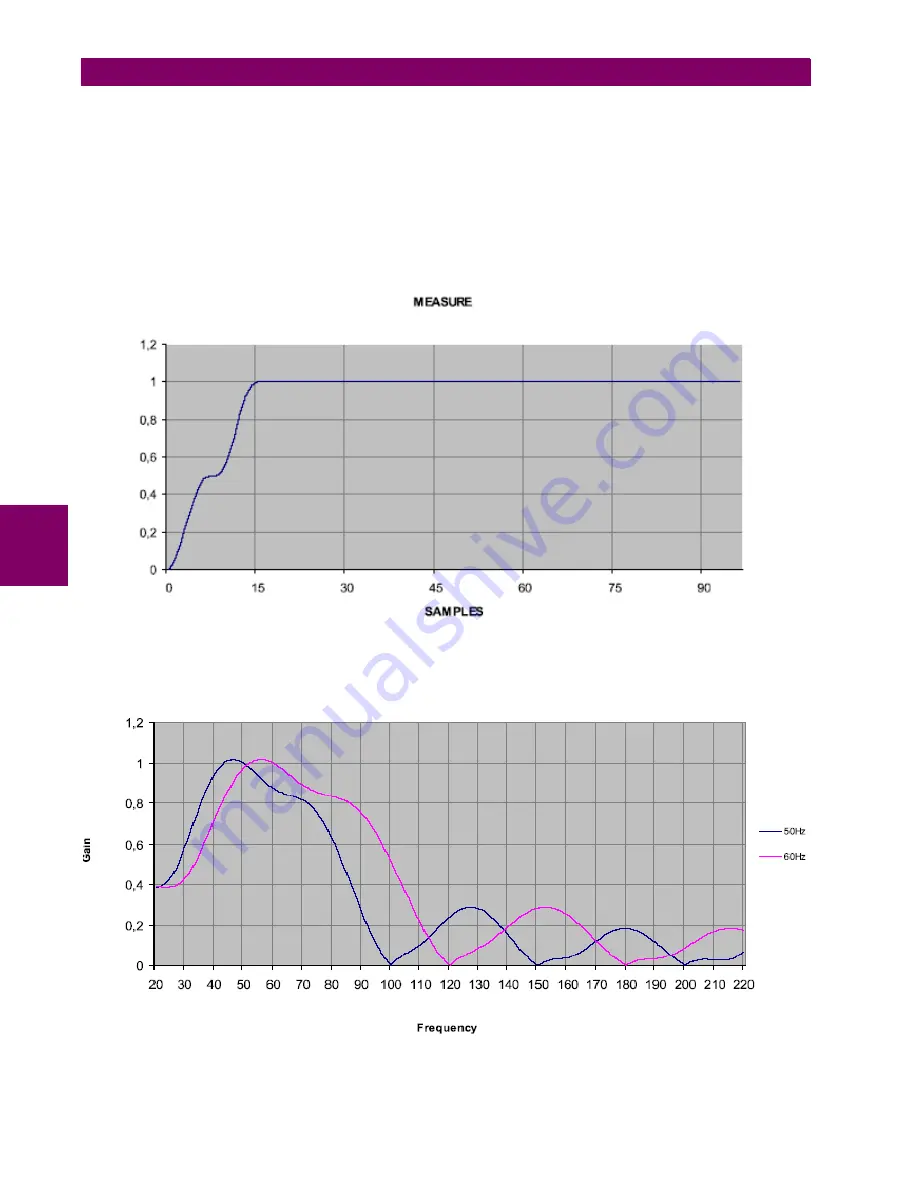
In the following figure, we can see how the measure is established from a signal value that changes from 0 to 1.
Figure C–2:
Figure C–3: shows the answer from the digital filter with the frequency. The figure shows how all the high level harmonics
are eliminated. This makes MIB suitable for applications where it is necessary to filter any type of harmonic, for example,
the 2nd and 3rd, which are the most commonly found in electrical lines.
Figure C–3:



































