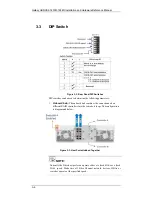
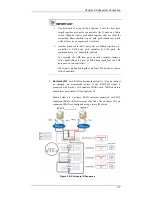
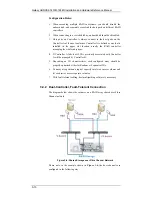
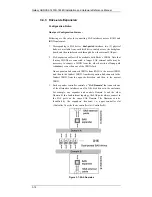
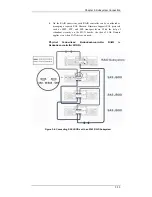
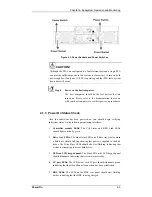
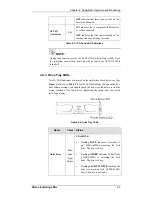
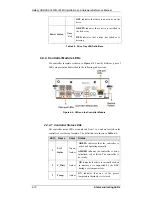
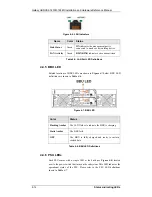
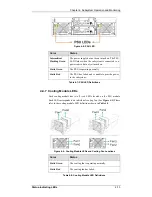
Reviews:
No comments
Related manuals for GHDXS2-1430R-16F4D

R3G175-AF01-02
Brand: ebm-papst Pages: 11

Tsi310TM
Brand: IDT Pages: 207

BOX Wi-Fi
Brand: NKE Pages: 15

DVI-PROWALL-9X
Brand: Avenview Pages: 28

TPMS1209T02-ER
Brand: S&T Pages: 28

Wisenet XRN-6410RB2-24TB
Brand: Hanwha Techwin Pages: 124

WAFER-ULT4
Brand: IEI Technology Pages: 136

U3024AH10
Brand: Keysight Technologies Pages: 106

HiGain Line Unit HLU-388
Brand: PairGain Pages: 7

X-FireWire Card
Brand: Apogee Pages: 32

Linktropy MINI-G
Brand: Apposite Technologies Pages: 57

H100i
Brand: Corsair Pages: 134

STEVAL-IHT003V1
Brand: ST Pages: 20

PEX8S952
Brand: StarTech.com Pages: 9

RACK2
Brand: Crestron Pages: 52

HSB1SATSASBA
Brand: StarTech.com Pages: 2

VTX-1
Brand: AMX Pages: 1

SRH-3000
Brand: Samsung Pages: 2