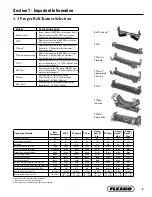
9
Section 6 - Maintenance
Flexco belt trainers are designed to operate with minimum maintenance. However, to maintain superior performance
some service is required. When the trainer is installed a regular maintenance program should be set up. This program
will ensure that the trainer operates at optimal efficiency, and problems can be identified and fixed before any damage
is done to the belt, the trainer, other conveyor components, or structure.
All safety procedures for inspection of equipment (stationary or operating) must be observed. The RBP1 Belt
Positioner is in direct contact with the moving belt. Only visual observations can be made while the belt is running.
Service tasks can be done only with the conveyor stopped and by observing the correct lockout/tagout procedures.
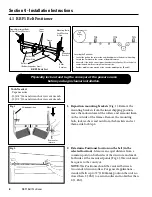
6.1 New Installation Inspection
After the RBP1 Belt Positioner has run for 15 minutes a visual inspection should be made to ensure the trainer
is performing properly. Make adjustments as needed.
6.2 Routine Visual Inspection (every 2-4 weeks)
A visual inspection of the RBP1 Belt Positioner can determine:
• If the belt is tracking as required
• If the main frame is free of material and rolling properly
• If there is damage to the main frame or other components
• If the rollers are turning freely and without damage
If any of the above conditions exist, a determination should be made on when the conveyor can be
stopped for trainer maintenance.
6.3 Routine Physical Inspection (every 6-8 weeks)
When the conveyor is not in operation and properly locked and tagged out, a physical inspection of the trainer
to perform the following tasks:
• Clean material buildup off the trainer and components.
• Closely inspect main roller for free movement and wear. Replace if needed.
• Closely inspect complete unit for damage.
• Inspect all fasteners for tightness and wear. Tighten or replace if needed.
• When maintenance tasks are completed, test run the conveyor to ensure the trainer is
performing properly.