4
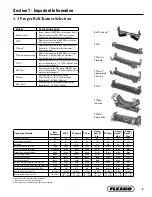
RBP1 Belt Positioner
Section 2 - Safety Considerations and Precautions
Before installing and operating the RBP1 Belt Positioner it is important to review and understand the following safety
information.
There are setup, maintenance and operational activities involving both stationary and operating conveyors. Each case
has a safety protocol.
2.1 Stationary Conveyors
The following activities are performed on stationary conveyors:
• Installation
• Impact bar replacement
• Repairs
• Skirt rubber adjustments
• Cleaning
DANGER
DANGER
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
!
!
!
!
!
It is imperative that OSHA/MSHA Lockout/Tagout
(LOTO) regulations, 29 CFR 1910.147, be followed before
undertaking the preceding activities. Failure to use LOTO
exposes workers to uncontrolled behavior of the impact
bed caused by movement of the conveyor belt. Severe
injury or death can result.
Before working:
• Lockout/Tagout the conveyor power source
• Disengage any takeups
• Clear the conveyor belt or clamp securely
in place
Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
• Safety eyewear
• Hardhats
• Safety footwear
Close quarters and heavy components create a
worksite that compromises a worker’s eyes, feet
and skull.
PPE must be worn to control the foreseeable
hazards associated with conveyor belt
components. Serious injuries can be avoided.
2.2 Operating Conveyors
There are two routine tasks that must be performed while the conveyor is running:
• Inspection of the sealing performance
• Dynamic troubleshooting
Every belt conveyor is an in-running nip hazard.
Never touch or prod an operating impact bed.
Conveyor hazards cause instantaneous amputation
and entrapment.
Never adjust anything on an operating impact
bed. Unforseeable materials falling into the chute
can cause violent movements of the impact bed
structure. Flailing hardware can cause serious
injury or death.
Conveyor chutes contain projectile hazards. Stay as far
from the trainer as practical and use safety eyewear and
headgear. Missiles can inflict serious injury.