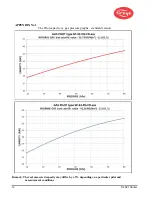
6
© 2021 Carrier
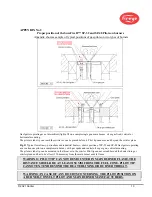
It should be remembered that the rod tip positioning against the stabilizer plate in the pilot gas part assembly
(pos. 3 on Fig.1) should be done outside the air tube only.
Only after proper rod positioning should the rod be fixed by tightening the gland and the whole gas assembly
with rod inserted into the air tube.
b)
Mounting of electrical igniter rod in a pilot: unscrew the rod tip, disassemble the gland, put all gland
parts on rod, insert the rod in gas head, screw back the rod tip and then set the appropriate tip position
relative to an orifice-stabilizer assy. Now the gland can be screwed onto gas head tightly.
In case of
problems in sliding the rod through rings of fixing gland apply a small amount of high temperature resistant
grease or grind slightly the gland ring inner surface.
After setting the correct rod position, fasten the rod fixing gland in the gas head. Then the complete gas part
assembly can be slid into the air tube.
Do not remove the rod from fixing gland if it is not necessary as the gland rings once clamped on rod do not
allow easy rod movement.
After setting the correct rod position, fasten the rod fixing gland in the gas head. Then the complete gas part
assembly can be slid into the air tube.
c)
Gas part assembly and air tube should be fastened by the mounting ring thread joint. Ensure that the ring
gasket is correctly fitted in the gas head seat (see Fig. 4).
d)
The complete pilot (air tube) can be inserted into the mounting tube. In order to make the air tube slide-in
easier, apply a small amount of high temperature resistant grease.
e)
The insertion depth of
SP-32-FD
pilot is determined by the design of the main burner.
If an existing pilot has to be replaced, the insertion length and pilot tip position should be the same.
In case of any doubts, the position of the pilot should be consulted with the pilot or burner manufacturer.
f)
After determining the position of the complete pilot relative to the mounting tube, the mounting tube
clamping screws should be tightened to prevent the device from moving.
FIGURE 4.
Gas head with ring gasket and orifice-stabilizer assembly
7.3 GAS AND AIR SUPPLY INSTALLATION
a)
The pilot must be set in the mounting tube such that the air and gas connections are in the desired position.
b)
Connect the air and gas hoses to the appropriate pilot inputs. Hoses cannot be tangled or twisted. If necessary,
additional connectors may be used.
c)
To ensure a long and trouble-free operation of the pilot it should be kept clean. Check the condition of the
gas pipe and if the orifices are not blocked. Remove all buildups. Hoses should be dry and not cracked.
d)
During service works, secure the disconnected ends of the hoses by closing the ends with a plug or a tape.
e)
Use the automatic shutoff valves of the appropriate size and the respective closing rate and pilot gas pressure
measurement with safety interlocks (compliant with the requirements of relevant standards concerning the
shut-off safety fuel valves and burner safety) to be sure that the gas delivered to the pilot is of an adequate
pressure and can be quickly and effectively shut off.
f)
Use manual shut-off valves on air and gas lines for each pilot in case of maintenance or replacement and for
adjustment of pressure and flow on each pilot separately.
7.4 CABLING
Wiring and electrical connections design and layout should be in accordance with the requirements for burner
installation devices specified in their instructions and the relevant regulations.