Design and function
Interfaces for automation
099-007021-EW501
29.07.2015
83
5.16 Interfaces for automation
CAUTION
Damage to the machine due to improper connection!
Unsuitable control leads or incorrect connection of input and output signals can cause
damage to the machine.
• Only use shielded control leads!
• If the machine is to be operated with control voltages connection via suitable isolation
amplifiers is required!
• To control the main or secondary current via control voltages, the relevant inputs must be
enabled (see specification for activation of control voltage).
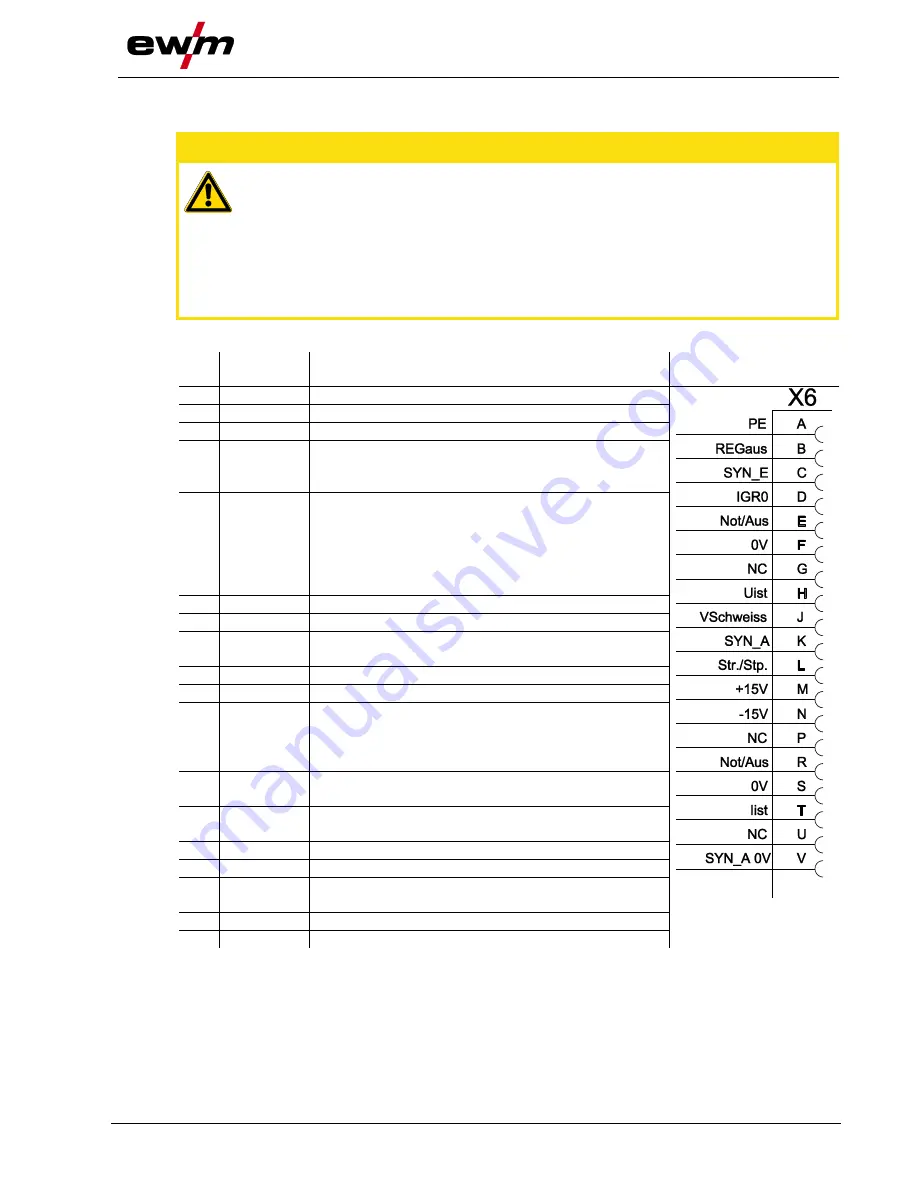
5.16.1 TIG interface for mechanised welding
Pin
Signal
shape
Designation
Diagram
A
Output
PE
Connection for cable screen
B
Output
REGaus
For servicing purposes only
C
Input
SYN_E
Synchronisation for master/slave operation
D
Input
(no c.)
IGRO
Current flows signal I>0 (maximum load
20mA / 15V)
0V = welding current flowing
E
+
R
Input
Output
Not/Aus
Emergency stop for higher level shut-down
of the power source.
To use this function, jumper 1 must be
unplugged on PCB T320/1 in the welding
machine. Contact open
welding current
off
F
Output
0V
Reference potential
G
-
NC
Not assigned
H
Output
Uist
Actual welding voltage, measured on pin F,
0-10V (0V = 0V, 10V = 100V)
J
Vschweiss Reserved for special purposes
K
Input
SYN_A
Synchronisation for master/slave operation
L
Input
Str/Stp
Start / stop welding current, same as torch
trigger.
Only available in non-latched operating
mode. +15V = start, 0V
stop
M
Output
+15V
Voltage supply
+15V, max. 75mA
N
Output
-15V
Voltage supply
-15V, max. 25mA
P
-
NC
Not assigned
S
Output
0V
Reference potential
T
Output
Iist
Actual welding current, measured on pin F;
0-10V (0V = 0A, 10V = 1000A)
U
NC
V
Output
SYN_A 0V Synchronisation for master/slave operation
















































