RX
−
8564
LC
Page
−
32
ETM12E-01
13.6. Reading/Writing Data via the I
2
C Bus Interface
13.6.1. Overview of I2C-BUS
The I
2
C bus supports bi-directional communications via two signal lines: the SDA (data) line and SCL (clock) line. A
combination of these two signals is used to transmit and receive communication start/stop signals, data transfer
signals, acknowledge signals, and so on.
Both the SCL and SDA signals are held at high level whenever communications are not being performed.
The starting and stopping of communications is controlled at the rising edge or falling edge of SDA while SCL is at
high level.
During data transfers, data changes that occur on the SDA line are performed while the SCL line is at low level, and
on the receiving side the data is output while the SCL line is at high level.
The I
2
C bus device does not include a chip select pin such as is found in ordinary logic devices. Instead of using a
chip select pin, slave addresses are allocated to each device and the receiving device responds to communications
only when its slave address matches the slave address in the received data. In either case, the data is transferred via
the SCL line at a rate of one bit per clock pulse.
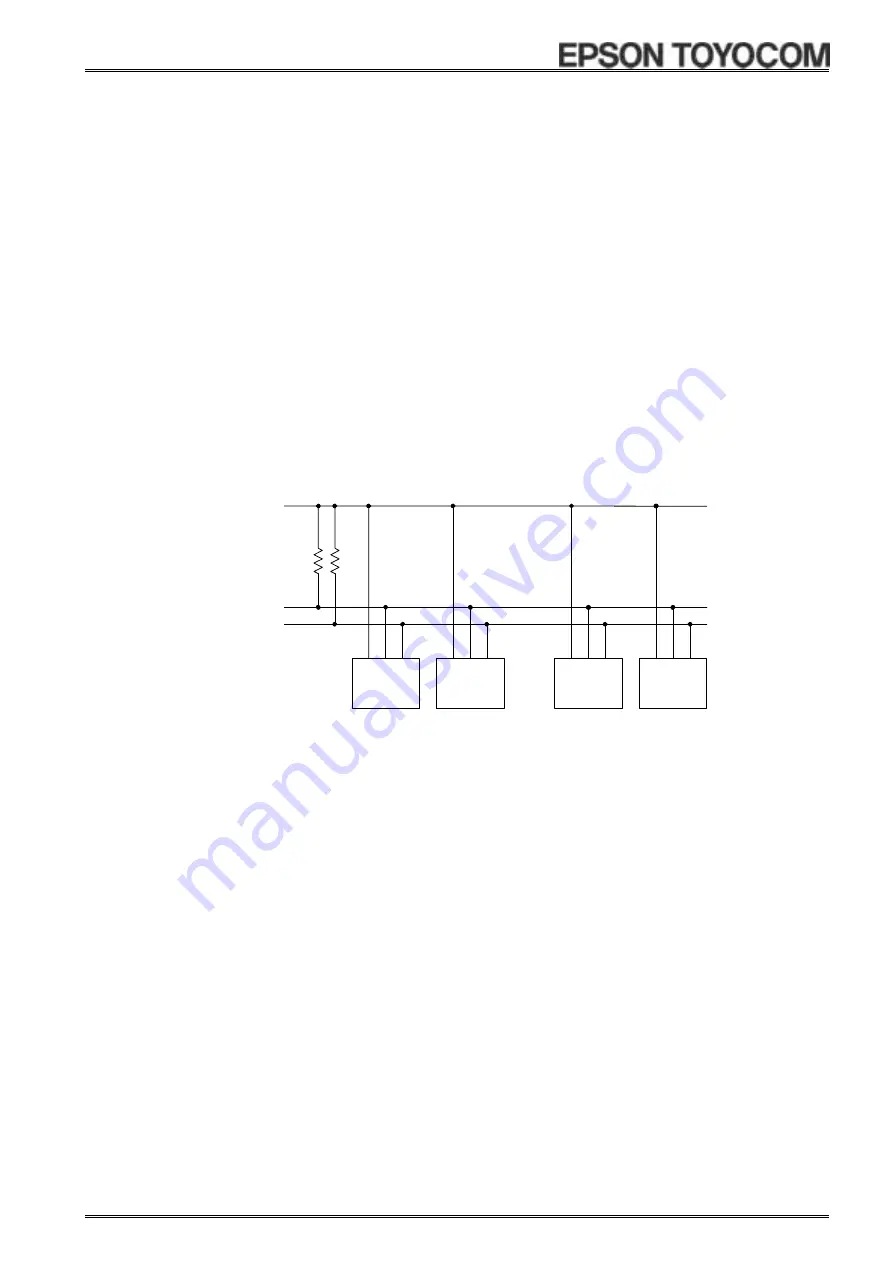
13.6.2. System configuration
All ports connected to the I
2
C bus must be either open drain or open collector ports in order to enable AND
connections to multiple devices.
SCL and SDA are both connected to the V
DD
line via a pull-up resistance. Consequently, SCL and SDA are both
held at high level when the bus is released (when communication is not being performed).
Master
Transmitter/
Receiver
Slave
Transmitter/
Receiver
Other I
2
C bus device
CPU, etc.
[
8564
]
SDA
SCL
V
DD
Master
Transmitter/
Receiver
Slave
Transmitter/
Receiver
Any device that controls the data transmission and data reception is defined as a "Master".
and any device that is controlled by a master device is defined as a “Slave”.
The device transmitting data is defined as a “Transmitter” and the device receiving data is defined as a receiver”
In the case of this RTC module, controllers such as a CPU are defined as master devices and the RTC module is
defined as a slave device. When a device is used for both transmitting and receiving data, it is defined as either a
transmitter or receiver depending on these conditions.





































