1592023040 XM668D GB r1.1 2011.07.05.doc
XM668D
6/14
second possibility, it can be used only in centralized plants and it is available
only with electronic expansion valve
by selecting [
CrE=Y
] parameter. The third
kind of regulation has been thought to be used with vales called evaporator valves
[
CrE=EUP
], in this configuration the valve is placed at the end of the evaporator. In
any case, the regulation is performed via PI regulator that gives the opening
percentage to the valve.
Standard regulation: [CrE=n]
In this case, the
HY
parameter is the differential for standard ON/OFF regulation. In
this case the
int
parameter is neglected.
Continuous regulation: [CrE=Y]
In this case, the
HY
parameter is the proportional band of PI in charge of room
temperature regulation and we advise to used at least [
HY = 5.0°C/10°F
]. The
int
parameter is the integral time of the same PI regulator. Increasing
int
parameter the
PI regulator become slowly in reaction and of course is true vice versa. To disable the
integral part of regulation you should set [
int=0
].
Evaporator valves: [CrE=EUP]
In this case, the system performs a regulation of the temperature without thinking
about the superheat (in fact the valve is at the end of the evaporator). The
HY
parameter is the proportional band for the temperature regulation and
int
is the
integral time for the regulation. In this situation there is no superheat regulation.
12.3
DEFROST
Defrost starting
In any case, the device check the temperature read by configured defrost probe
before starting defrost procedure, after that:
-
(If RTC is present)Two defrost modes are available through the
tdF
parameter:
defrost with electrical heater and hot gas defrost. The defrost interval is controlled
by parameter
EdF
: (
EdF=rtC
) defrost is made in real time depending on the hours
set in the parameters
Ld1
to
Ld6
in workdays and in
Sd1
to
Sd6
on holidays;
(
EdF=in
) the defrost is made every
idF
time.
-
Defrost cycle starting can be operated locally (manual activation by means of the
keyboard or digital input or end of interval time) or the command can come from
the Master defrost unit of the LAN. In this case the controller will operate the
defrost cycle following the parameters it has programmed but, at the end of the drip
time, will wait that all the other controllers of the LAN finish their defrost cycle
before to re-start the normal regulation of the temperature according to
dEM
parameter.
-
Every time any of the controller of the LAN begin a defrost cycle it issue the
command into the network making all the other controllers start their own cycle.
This allows a perfect synchronization of the defrost in the whole multiplexed
cabinet according to
LMd
parameter.
-
Differential defrost:
Selecting
dPA
and
dPb
probes and by changing the
dtP
and
ddP
parameters the defrost can be started when the difference between
dPA
and
dPb
probes is lower than
dtP
for all
ddP
time. This is useful to start defrost when a
low thermal exchange is detected. If [
ddP=0
] this function is disabled.
-
Defrost ending
-
When defrost is started via
rtC
, the maximum duration of defrost is obtained from
Md
parameter and the defrost end temperature is obtained from
dtE
parameter
(and
dtS
if two defrost probes are selected).
-
If
dPA
and
dPb
are present and [
d2P=Y
]
,
the instrument stops the defrost
procedure when
dPA
is higher than
dtE
temperature and
dPb
is higher than
dtS
temperature.
At the end of defrost the drip time is controlled through the
Fdt
parameter.
12.4
FANS
CONTROL WITH RELAY
The fan control mode is selected by means of the
FnC
parameter:
C-n
= running with the solenoid valve, OFF during the defrost;
C-Y
= running with th1e solenoid valve, ON during the defrost;
O-n
= continuous mode, OFF during the defrost;
O-Y
= continuous mode, ON during the defrost.
An additional parameter
FSt
provides the setting of temperature, detected by the
evaporator probe, above which the fans are always OFF. This can be used to make
sure circulation of air only if his temperature is lower than set in
FSt
.
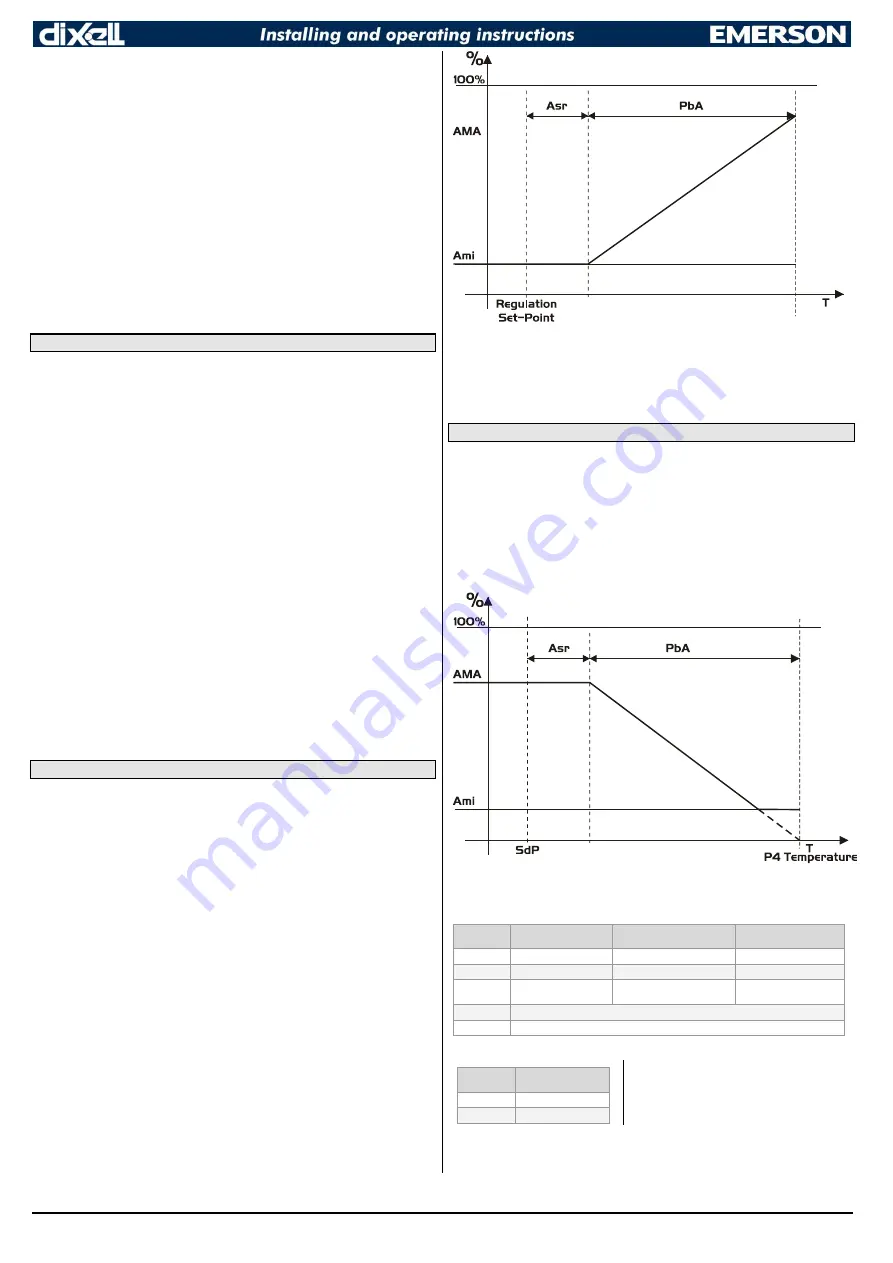
CONTROL WITH ANALOG OUTPUT (if present)
The modulating output [
trA=rEG
] works in proportional way (excluding the first
AMt
seconds where the fans speed is the maximum. 10seconds is the minimum value).
The regulation set point is relative to regulation set point and is indicated by
ASr
, the
proportional band is always located above [
SET+ASr
] value and its value is
PbA
.
The fans are at minimum speed
AMi
when the temperature read by fan probe is
[
SET+ASr
] and the fan is at maximum speed (
AMA
) when the temperature is
[
SET+ASr+PbA
].
12.5
ANTI SWEAT HEATERS
The anti-sweat heater regulation can be performed with on board relay (if
oA6=AC
)
or with the analog output (if present by setting
trA=AC
). However the regulation can
be performed in two ways:
Without real dew-point information: in this case the default value for dew-
point is used (
SdP
parameter).
Receiving dew-point from
XWEB5000
system: the
SdP
parameter is
overwritten when valid value for dew-point is received from XWEB. In
case of XWEB link is lost,
SdP
is the value that will be used for safety.
The best performance can be obtained using probe 4. In this case, the regulation
follows the chart:
Probe 4 should be placed on the showcase glass
. For each cabinet can be used
only one probe 4 (P4) sending its value to the others section that are connected to
the LAN.
HOW TO WORK WITH PROBE 4 THROUGH THE LAN:
Param.
XM6x8D_1
Without probe 4
XM
with
probe 4
XM
Without probe 4
Adr
n
n + 1
n + 2
LCP
LCP = n
LCP = Y
LCP = n
P4C
LAN or not
connect the probe
P4C = NTC, PtC or
PtM
LAN or not connect
the probe
trA
trA = AC if the device has the analog output
oA6
oA6 = AC if the device will use the AUX relay for regulation
HOW TO WORK WITHOUT PROBE 4:
Param.
XM6x8D
Without probe 4
P4C
nP
AMt
% of ON
In this case, the regulation is performed by
switching on and off the auxiliary relay on a
60 minutes time base. The ON time will be
the
AMt
value, so that the relay will be ON for
AMt
minutes and OFF for
[60-AMt]
minutes.
In case of P4 error or if P4 is absent the output is at
AMA
value for the
AMt
time then
the output is at 0 value for the time [
255–AMt
] time performing a simple PWM
modulation.
































