G
‐
MAS
–
Gold
Maestro
Software
User’s
Manual
Software
User
Manual
XXXXXXXXXXXX(0.01)
4
‐
54
4.3.
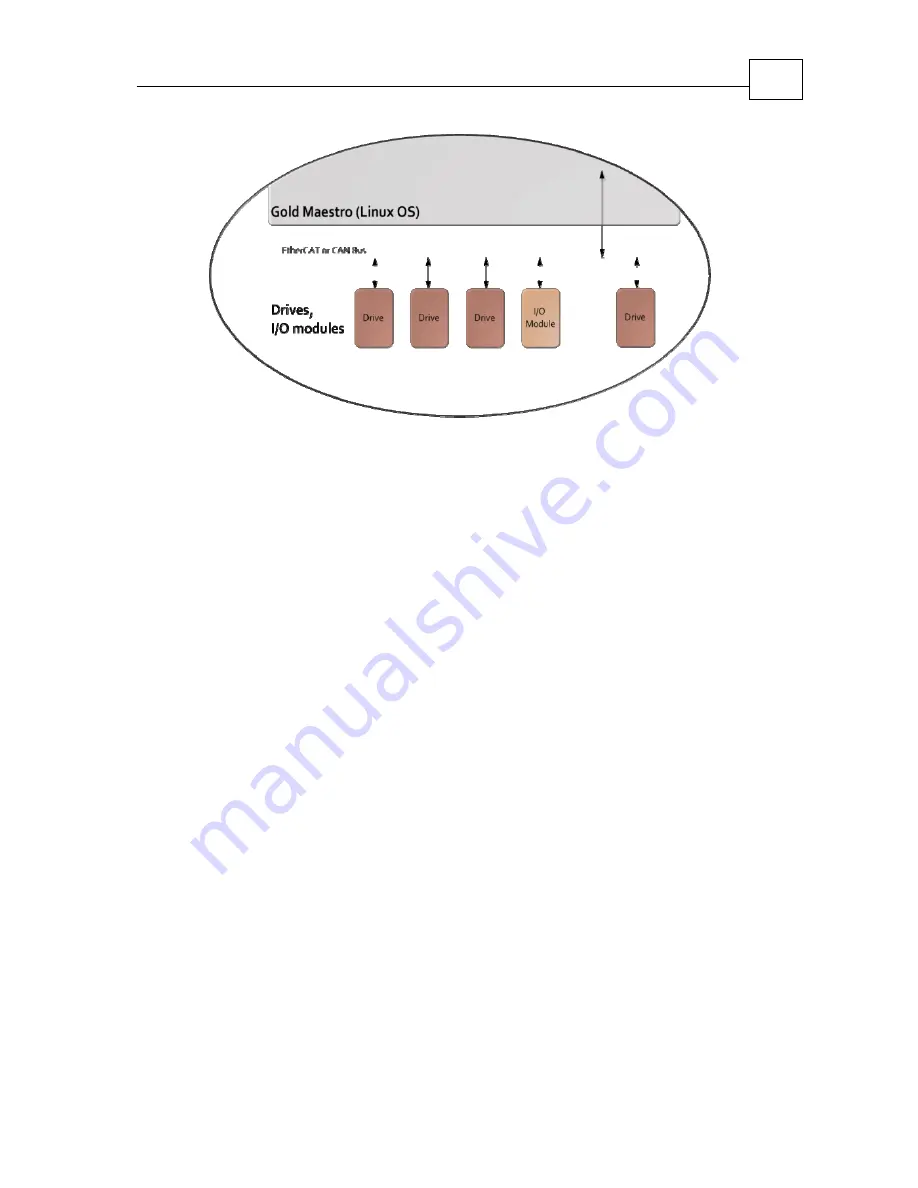
The device network
In
general,
the
overall
motion
control
system
is
designed
to
move
motors
and,
if
necessary,
to
control
the
machine’s
I/Os.
Motors
and
I/Os
are
interfaced
to
the
system
using
Servo
Drives
and
I/O
controllers
(only
if
required,
as
each
of
the
Servo
Drives
supports
a
number
of
I/Os
for
general
purposes).
These
end
‐
units
(servo
drives,
I/Os
controllers,
network
encoders,
etc.)
are
connected
to
the
G
‐
MAS
over
a
Device
Network.
The
G
‐
MAS
supports
one
of
two
Device
Networks:
CAN
or
EtherCAT.
The
G
‐
MAS
Firmware
is
responsible
to
manage
the
Device
Network
and
to
perform
all
required
communications
in
a
synchronous
manner
and
according
to
the
standards
of
this
network.
Generally
speaking,
the
user
does
not
need
to
know
the
details
of
the
device
network
as
all
the
details
are
automatically
handled
by
the
G
‐
MAS.
The
exact
list
of
protocols
supported
by
each
of
these
two
networks,
as
well
as
the
specifications
of
each
protocol
(minimal
update
time,
delays,
etc.)
is
included
within
the
G
‐
MAS
User’s
Manual.
4.4.
Additional tools
The
above
‐
described
structure
of
a
G
‐
MAS
based
system
is
a
simplified
structure.
It
does
not
include
some
additional
software
tools
that
may
be
required
for
setup
and
configuration
of
the
G
‐
MAS.
This
chapter
describes
these
additional
tools.
4.4.1.
KPA Studio
The
G
‐
MAS
EtherCAT
Configuration
is
used
to
initially
scan
the
EtherCAT
bus
and
locate
the
controllers
on
the
bus,
configure
the
Input
/
Output
process
cycle
parameters,
check
the
EtherCAT
bus
(CRC
errors)
and
download
the
EtherCAT
configuration
resource
file
to
the
G
‐
MAS.
4.4.2.
IP Configuration over USB
TBD




































