System Overview
2-4
SkyView SE
Pilot’s User Guide
- Revision B
GPS
Pi
to
t
Stat
ic
A
OA
M
ag
n
e
to
m
e
te
rs
R
ate
Se
n
sor
s
A
cc
e
le
ro
m
e
te
rs
OA
T
Ex
te
rna
l
ma
gn
eto
me
te
r
Ball
✓
Altitude
✓
Airspeed
✓
✓
AOA
✓
✓
Turn Rate
✓
✓
✓
✓
Heading
✓
✓
✓
**
✓
✓
✓
Attitude
✓
*
✓
✓
✓
✓
Density
Altitude
✓
✓
TAS
✓
✓
✓
Winds
✓
✓
✓
✓
**
✓
✓
Ground
Speed
✓
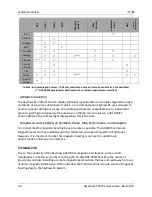
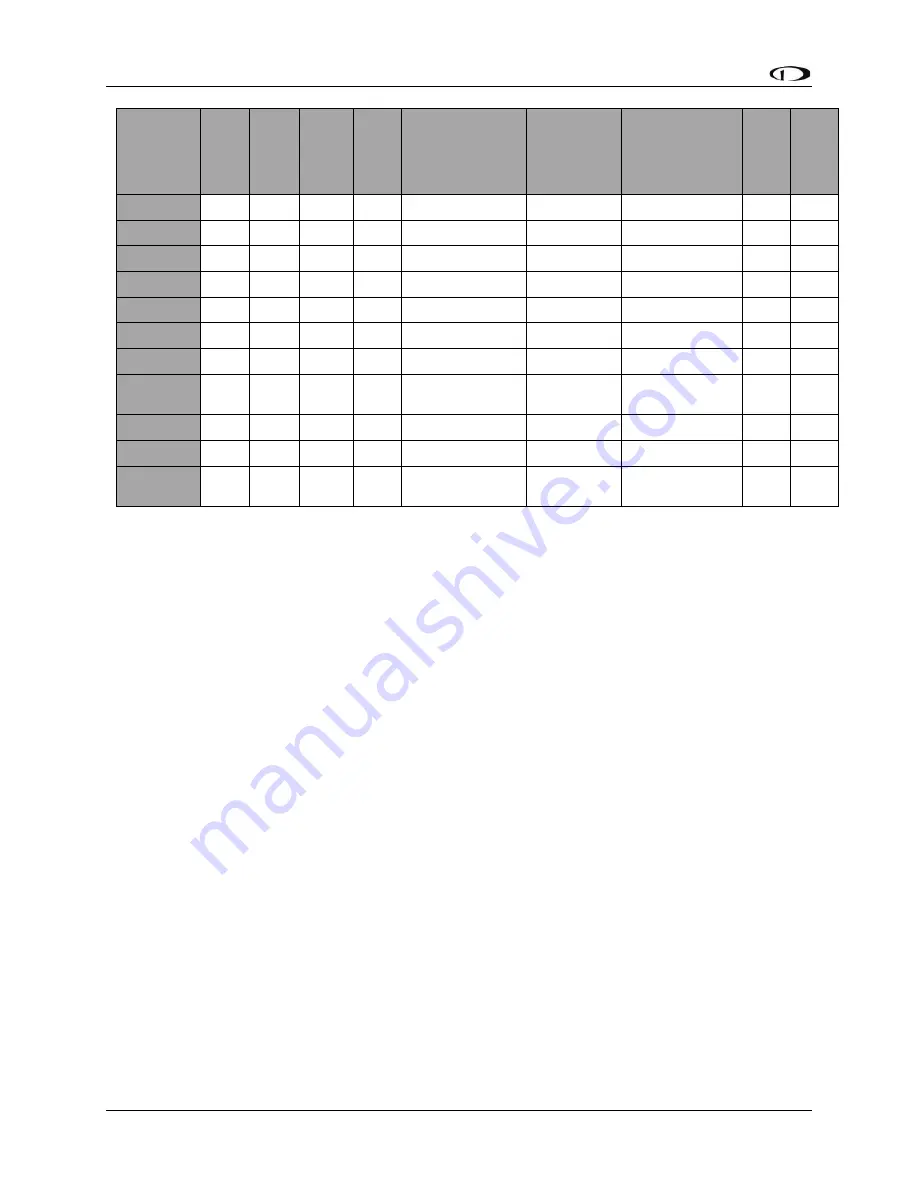
Table 2
–
Instruments and Sensors (*GPS only used when airspeed from pitot and static is not available)
(** ADAHRS Magnetometer deactivated when remote magnetomber installed)
Attitude Calculation
The SkyView SE artificial horizon display (attitude) is generated via a complex algorithm using a
multitude of sensors as described in Table 2. In normal operation SkyView SE uses airspeed to
provide superior attitude accuracy. Should airspeed become unavailable due to inadvertent
pitot icing, GPS ground speed will be used as an attitude aid. You will see a GPS ASSIST
annunciation on the primary flight display when this is the case.
Compass Accuracy Effects on Synthetic Vision, Map Performance, and Autopilot
It is critical that the magnetic heading be as accurate as possible. The ADAHRS or Remote
Magnetometer must be installed correctly, calibrated, and operating well
in all attitudes
.
However, it is important to note that magnetic heading is not used to aid attitude
determination under any circumstance.
SV-MAG-236
Due to the sensitivity of the SkyView ADAHRS to magnetic interference, some aircraft
installations are better served by mounting the SV-ADAHRS-200/201 within the center of
gravity box and also installing a remote magnetometer outside the box and well away from any
dynamic magnetic interference. When installed, the SV-MAG-236 is the sole source of magnetic
heading data to the SkyView SE System.