Air-to-open valve
5.
Shut-off supply pressure. Valve plug should be
seated.
6.
Proceed with the calibration, performing step 9
described below.
Air-to-close valve
7.
Adjust supply pressure to proper requirement (psig).
(See valve catalog for proper supply pressure
according to valve size and to pressure drop; see
also the serial plate).
8.
With a 10 mm flat wrench unscrew about one turn
the metering tube assembly (59) until valve plug is
seated.
On an air-to-close valve and
on an air-to-open valve
9.
When the valve stem is in contact with the seat
(valve seated) loosen the screw (160) in order that
cam will rotate.
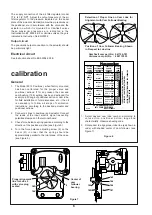
10. Select proper cam lobe and lobe line referring to
Figure 6. Rotate cam to align proper lobe line with
center of cam follower bearing as indicated in
Figure 7. Tighten screw (160) to maintain the
relation-ship of cam to cam follower.
11. If air supply is shut off (air-to-open valve) then
adjust supply pressure to proper psig (see valve
catalog or the serial plate). If air-to-close valve,
tighten metering tube assembly (59). (Tighten firmly
but do not overtighten).
12. Adjust signal to proper value corresponding to valve
closed position.
13. Adjust the biasing spring (52) so that the valve plug
will lift off the seat at the proper closing milliamp
signal.
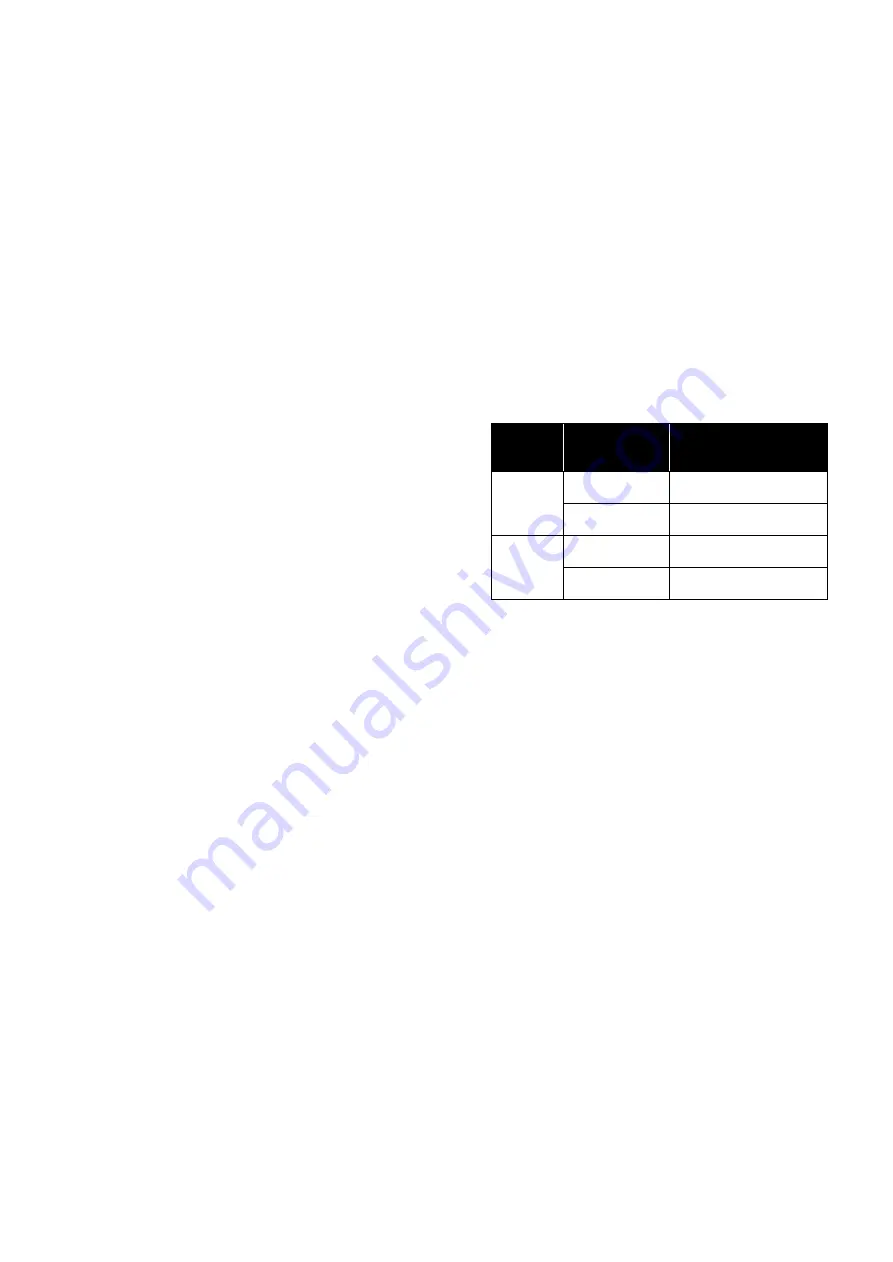
14. Check full valve stroke for full signal span. If stroke
is too short for full signal span or if valve reaches full
stroke before full signal span (stroke is too long)
adjust force balance spring screw (6) as indicated in
table below. After adjusting force balance spring,
repeat steps 12, 13 and 14 until proper valve stroke
is obtained for full signal span.
15. Assemble cover (3) and cam cover (151).
7
maintenance
Warning :
De-energize electric and pneumatic circuits before
service or maintenance. Be sure that connections
are correctly performed and that the cover is well
placed on the case before energizing the circuits.
Only qualified personnel to service this equipment.
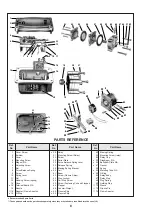
Metering tube
The metering tube (59) for the nozzle air supply is
furnished with a clean-out plunger which forces a small
wire through the jewel orifice. The metering assembly
can be removed and checked prior to relay disassembly.
Relay disassembly
1.
Disconnect air tubing. Unscrew the four relay
mounting screws (21) and remove relay from the
case (14).
2.
Remove holding screw (69) and drop the plug (67)
and spring (68) from the relay body (66).
3.
Remove the six screws (53) which hold the relay
cap (54), diaphragm S/A (55) and Bellofram plate
(56), gasket (57) and spring (58) to the relay body.
Clean parts with a clean soft cloth. Use solvent if oil
or grease is present (do not use solvent on
diaphragms). Blow out parts with clean dry air.
Replace all damaged parts.
Relay reassembly
1.
Replace spring (58) and position gasket (57) on the
relay body. Place Bellofram plate S/A (56),
diaphragm S/A (55) and cap (54). Align holes in this
elements with those of the relay body (66). Correct
alignment is simplified by use of external reference
mark. Insert two screws 180° apart through this
assembly. Replace and tighten the six screws (53).
2.
Assemble relay plug (67), spring (68) and holding
screw (69). Establish correct position of relay and
fasten on the positioner case. If relay repairs are
required it is recommended that a new temporary
relay be adapted, permitting to minimize time out of
service.
Nozzle
To clean nozzle (16) shut off air supply ; loosen screw
(45) and remove flapper (46) from beam (41).
Unscrew nozzle (16) from case. Clean out hole with
solvent and clean dry air. Screw nozzle into the case,
replace flapper on the beam and tighten screw (45).
If Stroke
is :
And Positioner
Action is :
Turn Force Balance
Spring Adjusting
Screw (6) :
Too
short
Direct
Counter clockwise
rotation
Reverse
Clockwise
rotation
Too
long
Direct
Clockwise
rotation
Reverse
Counter clockwise
rotation