DES-3326S Layer 3 Fast Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
54
Switch Management and Operating Concepts
they must immediately take certain actions to avoid future
failure or breakdown of the network.
You can also specify which network managers may receive
traps from the Switch by entering a list of the IP addresses of
authorized network managers. Up to four trap recipient IP
addresses, and four corresponding SNMP community strings
can be entered.
SNMP community strings function like passwords in that the
community string entered for a given IP address must be used
in the management station software, or a trap will be sent.
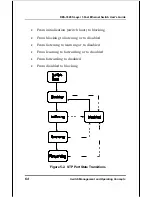
The following are trap types the switch can send to a trap
recipient:
•
Cold Start
This trap signifies that the Switch
has been powered up and initialized such
that software settings are reconfigured and
hardware systems are rebooted. A cold start
is different from a factory reset in that
configuration settings saved to non-volatile
RAM used to reconfigure the switch.
•
Warm Start
This trap signifies that the
Switch has been rebooted, however the POST
(Power On Self-Test) is skipped.
•
Authentication Failure
This trap signifies
that someone has tried to logon to the switch
using an invalid SNMP community string. The
switch automatically stores the source IP
address of the unauthorized user.
•
Topology Change
A Topology Change trap is
sent by the Switch when any of its configured
ports transitions from the Learning state to
the Forwarding state, or from the Forwarding
state to the Blocking state. The trap is not