BT17i
Blood Pressure User’s Guide
|
3
How the Blood Pressure Sensor works
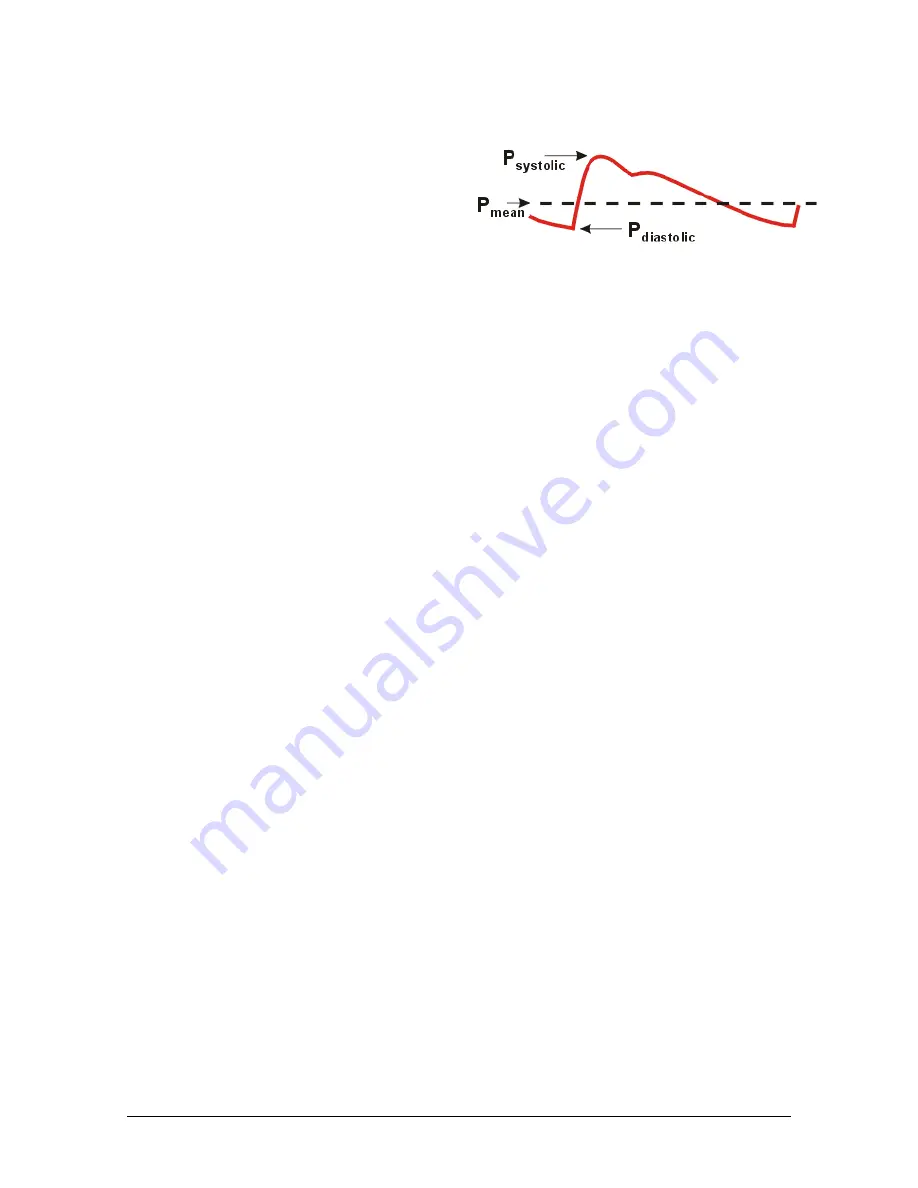
1. About blood pressure
During each heart beat the arterial blood
pressure varies between two utmost values:
the systolic and the diastolic pressure. The
peak pressure in the arteries is the systolic
pressure and the lowest pressure is the
diastolic pressure. In between these is the
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP), which is
used to describe the average blood
pressure.
2. Oscillometric method
The blood pressure sensor allows determining blood pressure via the so-called
oscillometric method. With this non-invasive method, a cuff is placed around the arm
and inflated by means of a pump, after which the cuff deflates via a control valve. The
sensor measures the pressure of the air in the cuff.
With inflation of the cuff, the external pressure on the artery rises. At pressures
exceeding the systolic blood pressure, the artery will be occluded, no blood flow occurs
through the artery. When the cuff is slowly deflated, the cuff pressure, and hence the
external pressure on the artery will be lowered to that of the systolic blood pressure.
Now, the artery is no longer continuously occluded. At systolic blood pressure, small
amounts of blood flow through the compressed artery and cause changes in the artery
volume, conducted to the cuff. This leads to detectable pressure oscillations in the cuff.
These oscillations increase with lower cuff pressure values, as more blood passes
through the compressed artery. The maximum oscillation amplitude is reached around
the mean arterial blood pressure. Then, as the pressure decreases until the cuff
becomes fully deflated, the blood flow returns to normal and the oscillation amplitude
decreases and small pulses remain at a low level below diastolic pressure.
A similar method is used during the regular blood pressure measurement, a clinician,
using the stethoscope, listens at the brachial artery for characteristics sounds of the
pressure pulses (so-called Korotkoff sounds).
Measurements with the Blood Pressure sensor
Safety instructions
The cuff is put around the upper arm and produces pressure on the brachial artery. To
reduce the risk on injuries and pain it is important to read and follow the following
safety instructions:
•
Put on the cuff as described in the next section of the manual.
•
Do not inflate the cuff to a pressure above 180 mmHg.
Over inflation of the cuff
may cause pain and/or injury
.
•
Deflate the cuff immediately using the control valve when the pressure in the cuff
exceeds 200 mmHg.
•
Measurements with the cuff around the upper arm should
not take longer than 3
minutes
. In any case deflate the cuff immediately using the control valve when the
Figure 1
. Pressure course of the heart beat in
the brachial artery.




























