Spanning Tree
STP Port Settings
Cisco Small Business SLM Series Smart Switches Administration Guide
59
7
To open the
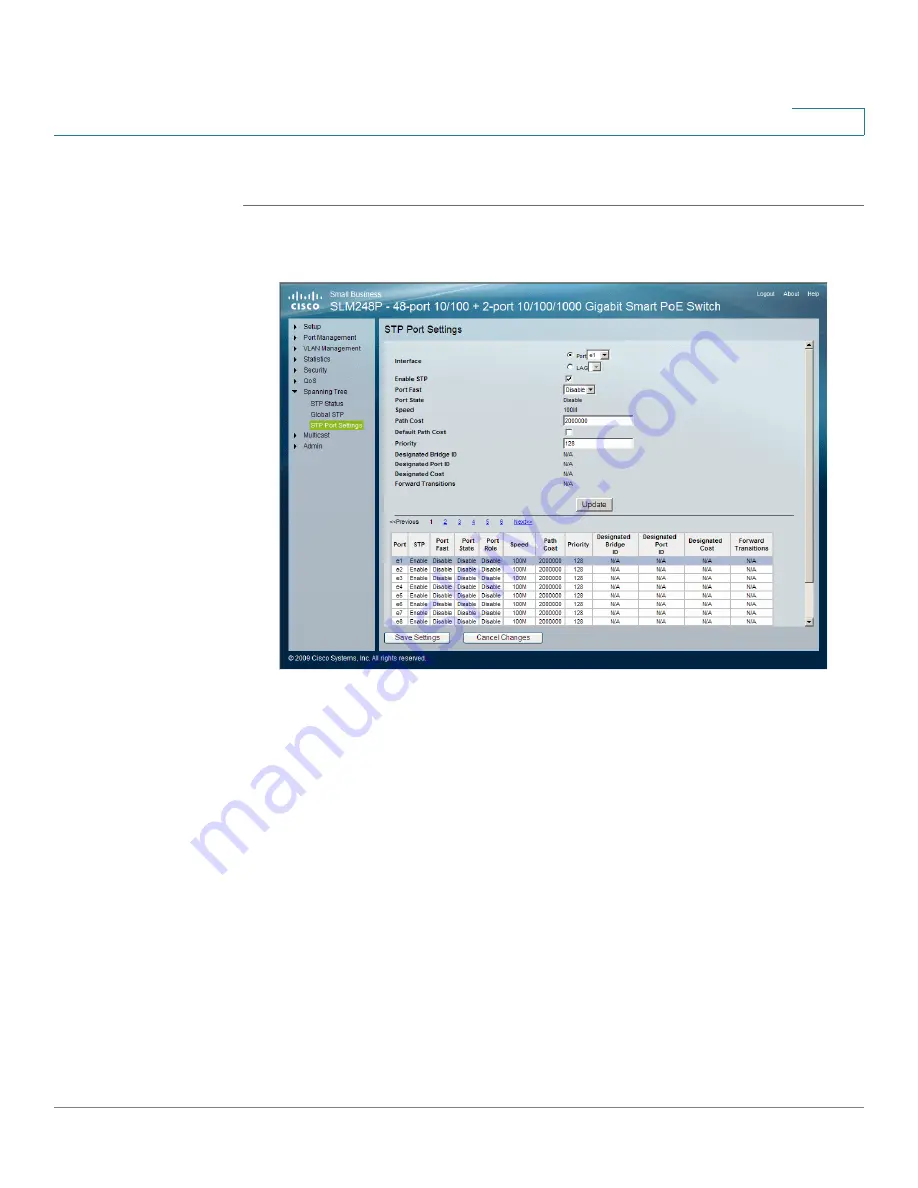
STP Port Settings
window:
STEP 1
Click Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings. The
STP Port Settings
window appears.
STP Port Settings
The
STP Port Settings
window contains the following fields:
•
Interface — Indicates the interface on which STP parameters are
configured. The possible field values are:
-
Port
— Indicates the port on which STP is configured.
-
LAG
— Indicates the LAG on which STP is configured.
•
Enable STP — Indicates if STP is enabled on the port. Select this field to
enable STP.
•
Port Fast — Indicates if Fast Link is enabled on the port. If Fast Link mode is
enabled for a port, the Port State is automatically placed in the Forwarding
state when the port link is up. Fast Link optimizes the STP protocol
convergence. STP convergence can take 30 seconds in large networks.
The possible field values are:
-
Enable
— Indicates that Fast Link is enabled on the port.






























