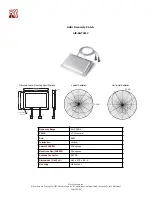
Cisco Systems, Inc.
All contents are Copyright © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.
Page 12 of 29
Regulations
North America
• Connectors—In 1985, the FCC enacted standards for the commercial use of spread spectrum technology in the ISM frequency
bands. Spread spectrum is currently allowed in the 900, 2400, and 5200 MHz bands. In 1989, the FCC drafted an amendment
governing spread spectrum systems in the unlicensed ISM band. This amendment is commonly referred to as the “new” or “’94”
rules because it impacts all spread spectrum products manufactured after June 23, 1994. Products manufactured before June 23
are not affected by the amendment. Congress enacted this amendment into law in 1990. The FCC 1994 rules are intended to
discourage use of amplifiers, high-gain antennas or other means of significantly increasing RF radiation. The rules are further
intended to discourage “home brew” systems which are installed by inexperienced users and which-either accidentally or
intentionally-do not comply with FCC regulations for use in the ISM band. Both the original rules and the amendments sought
to enable multiple RF networks to “coexist” with minimum impact on one another by exploiting properties of spread spectrum
technology. Fundamentally, the FCC 1994 rules intend to limit RF communications in the ISM band to a well defined region,
while ensuring multiple systems can operate with minimum impact on one another. These two needs are addressed by limiting
the type and gain of antennas used with a given system, and by requiring a greater degree of RF energy “spreading.”
• Antenna Gain and Power Output—FCC regulations specify maximum power output and antenna gain. At 2.4GHz the
maximum transmitter power is 1watt, or 30dBm. Using this maximum power, the maximum antenna gain is 6dBi. However,
the regulations also define the maximum values in regards to the following two different system scenarios.
In Point-to-Multipoint systems, the FCC has limited the maximum EIRP (effective isotropic radiated power) to 36dBm. EIRP =
TX power + antenna gain. For every dB that the transmitter power is reduced, the antenna may be increased by 1dB. (29dBm
TX, +7dB antenna = 36dBm EIRP, 28dBm TX, +8dB antenna = 36dBm EIRP).
The Cisco Aironet Bridge transmitter power is 20dBm, which is 10dBm lower than maximum. This then allows the use of
antennas up to 10dB over the initial 6dBi limit, or 16dBi.
In Point-to-Point systems for 2.4GHz systems, using directional antennas, the rules have changed. Because a high gain antenna
has a narrow beamwidth, and therefore the likelihood is high that it will cause interference to other area users. Under the rule
change, for every dB the transmitter is reduced below 30dBm, the antenna may be increased from the initial 6dBi, by 3dB. (29dB
Transmitter means 9dBi antenna, 28dB transmitter means 12dBi antenna). Because we are operating at 20dBm, which is 10dB
below the 30dBm level, we can increase the out antenna by 30dB. However Cisco has never tested, and therefore is not certified
with any antenna larger than 21dBi.
The main issue concerns what components comprise a point-to-point and multipoint system.
In Figure 7, Point A communicates to a single point, B, and Point B communicates to a single point A. Therefore it is simple to
see that both locations see this as a point to point installation.
In Figure 8, Point A communicates to more than one, or multiple points. Therefore Point A is operating in a multipoint
configuration, and the largest antenna permitted is 16dBi. Point B or Point C can each communicate to only one point, (Point A).
Therefore Point B and Point C actually operate in a single point or point-to-point operation, and a larger antenna may be used.
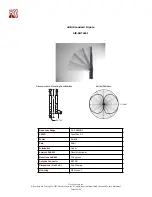
Figure 7
Point-to-Point Wireless Bridge Solution
A
B