Cisco Systems, Inc.
All contents are Copyright © 2003 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.
Page 11 of 29
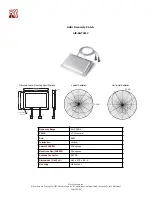
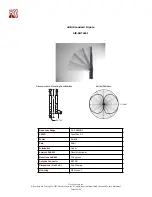
Fresnel Zone
Fresnel zone is an elliptical area immediately surrounding the visual path. It varies depending on the length of the signal path and
the frequency of the signal. The Fresnel zone can be calculated, and it must be taken into account when designing a wireless link.
Figure 6
Fresnel Zone
Based on both line of sight and Fresnel zone requirements, the following table provides a guideline on height requirements for
antennas as various distances. This refers to height above any obstacles located in the middle of the RF path.
Table 3
Cisco.com provides an Outdoor Bridge Range Calculation Utility that calculates the Fresnel zone and maximum range based upon
cable types and lengths; transmitter and receiver models; and antennas. The utility can be found at:
www.cisco.com/go/aironet/calculation.
Note that as path loss increases and distance decreases with frequency, these distances are only applicable to the 2.4 GHz band. A
10dB fade margin is included for dependable communications in all weather conditions. The distances given are only theoretical
and should only be used to determine the feasibility of a particular design.
Outdoors, every increase of 6 dB will double the distance. Every decrease of 6 dB will halve the distance. Shorter cable runs and
higher gain antennas can make a significant difference to the range.
Wireless Link Distance
(miles)
Approx. Value “F” (60%
Fresnel Zone) ft. at 2.4 GHz
Approx. Value “C”
(Earth Curvature)
Value “H” (mounting Ht.)
ft. with no obstructions
1
10
3
13
5
30
5
35
10
44
13
57
15
55
28
83
20
65
50
115
25
72
78
150
Fresnel Zone
Raise Antennas