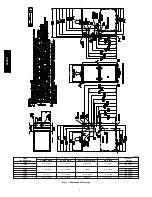
10
c.
TWO HORIZONTAL DUCTS
require 1 sq. in. (645 sq.
mm) of free area per 2,000 Btuh (1,100 mm
2
/kW) of com-
bined input for all gas appliances in the space per Fig. 6 and
Table 3.
d.
TWO OPENINGS OR VERTICAL DUCTS
require 1
sq. in. (645 sq. mm) of free area per 4,000 Btuh (550
mm
2
/kW) for combined input of all gas appliances in the
space per Fig. 6 and Table 3.
3.
ONE OUTDOOR OPENING
requires:
a. 1 sq. in. (645 sq. mm) of free area per 3,000 Btuh (734
mm
2
/kW) for combined input of all gas appliances in the
space per Fig. 6 and Table 3.
b. Not less than the sum of the areas of all vent connectors in
the space.
The opening shall commence within 12 in. (300 mm) of the
ceiling. Appliances in the space shall have clearances of at least 1
in. (25 mm) from the sides and back and 6 in. (150 mm) from the
front. The opening shall directly communicate with the outdoors or
shall communicate through a vertical or horizontal duct to the
outdoors or spaces (crawl or attic) that freely communicate with the
outdoors.
Indoor Combustion Air
E
NFPA & AGA
Standard and Known--Air--Infiltration Rate Methods
Indoor air
is permitted for combustion, ventilation, and dilution, if
the
Standard
or
Known--Air--Infiltration
Method is used.
CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
Many homes require air to be supplied from outdoors
for furnace combustion, ventilation, and dilution of flue
gases.
The furnace combustion air supply must be provided in
accordance with this instruction manual.
!
WARNING
Standard Method
1. The space has no less volume than 50 cubic feet per 1,000
Btuh of the maximum input ratings for all gas appliances
installed in the space and
2. The air infiltration rate is not known to be less than 0.40 air
changes per hour (ACH).
The
Known Air Infiltration Rate
Method shall be used, if the
infiltration rate is known to be:
1. Less than 0.40 ACH and
2. Equal to or greater than 0.10 ACH
Infiltration rates greater than 0.60 ACH shall not be used. The
minimum required volume of the space varies with the number of
ACH and shall be determined per Table 4 or Equations 1 and 2.
Determine the minimum required volume for each appliance in the
space and add the volumes together to get the total minimum
required volume for the space.
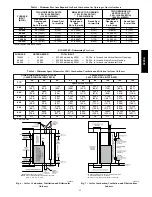
Table 4 -- Minimum Space Volumes were determined by using the
following equations from the current edition of the
National Fuel
Gas Code ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54, 9.3.2.2:
1. For other than fan--assisted appliances, such as a draft
hood--equipped water heater:
Volume
Other
= 21ft
3
ACH
I
other
1000 Btu/hr
A04002
2. For fan--assisted appliances such as this furnace:
Volume
Fan
= 15ft
3
ACH
I
fan
1000 Btu/hr
A04003
If: Iother = combined input of all other than fan--assisted appliances
in Btuh/hr
Ifan = combined input of all fan--assisted appliances in Btuh/hr
ACH = air changes per hour (ACH shall not exceed 0.60.)
The following requirements apply to the
Standard
Method and to
the
Known Air Infiltration Rate
Method.
1. Adjoining rooms can be considered part of a space if:
a. There are no closeable doors between rooms.
b. Combining spaces on same floor level. Each opening shall
have free area of at least 1 in.
2
/1,000 Btuh (2,000 mm
2
/kW)
of the total input rating of all gas appliances in the space,
but not less than 100 in.
2
(0.06 m
2
). One opening shall
commence within 12 in. (300 mm) of the ceiling and the
second opening shall commence within 12 in. (300 mm)
of the floor. The minimum dimension of air openings shall
be at least 3 in. (80 mm). See Fig. 7.
c. Combining space on different floor levels. The volumes of
spaces on different floor levels shall be considered as com-
municating spaces if connected by one or more permanent
openings in doors or floors having free area of at least 2
in.
2
/1,000 Btuh (4,400 mm
2
/kW) of total input rating of
all gas appliances.
2. An attic or crawlspace may be considered a space that freely
communicates with the outdoors provided there are ad-
equate permanent ventilation openings directly to outdoors
having free area of at least 1--in.
2
/4,000 Btuh of total input
rating for all gas appliances in the space.
3. In spaces that use the
Indoor Combustion Air
Method, in-
filtration should be adequate to provide air for combustion,
permanent ventilation and dilution of flue gases. However,
in buildings with unusually tight construction, additional air
MUST be provided using the methods described in the
Outdoor Combustion Air
Method section.
4. Unusually tight construction is defined as Construction
with:
a. Walls and ceilings exposed to the outdoors have a continu-
ous, sealed vapor barrier. Openings are gasketed or sealed
and
b. Doors and openable windows are weatherstripped and
c. Other openings are caulked or sealed. These include joints
around window and door frames, between sole plates and
floors, between wall--ceiling joints, between wall panels,
at penetrations for plumbing, electrical and gas lines, etc.
Combination of Indoor and Outdoor Air
1. Indoor openings shall comply with the
Indoor Combus-
tion Air
Method below and,
2. Outdoor openings shall be located as required in the
Out-
door Combustion Air
Method mentioned previously and,
3. Outdoor openings shall be sized as follows:
a. Calculate the Ratio of all Indoor Space volume divided by
required volume for
Indoor Combustion Air
Method be-
low.
b. Outdoor opening size reduction
Factor
is 1 minus the
Ra-
tio
in a. above.
c. Minimum size of Outdoor openings shall be the size re-
quired in
Outdoor Combustion Air
Method above multi-
plied by reduction
Factor
in b. above. The minimum di-
mension of air openings shall be not less than 3 in. (80 mm).
922SA