40
NOTE
: If the Maximum Vent Length for diameter of the pipe
selected is longer than the measured length and the equivalent
length of all the fittings and terminations (TEVL), recalculate
Total Equivalent Vent Length using the next smaller diameter. If
the Maximum Equivalent Vent Length is still longer than the
longer TEVL of the vent pipe or combustion air pipe, then that
diameter of pipe selected may be used.
When installing vent systems pipe lengths of 10 ft. (3 M) or less,
use the smallest allowable pipe diameter. Using a pipe size greater
than required for short venting systems may result in loss of
efficiency, incomplete combustion, flame disturbance, or flame
sense lockout.
For vent systems longer than 10 ft. (3 M), any larger diameter vent
pipe shown in Table 16
FOR THAT SIZE FURNACE
may be
used.
Combustion Air and Vent Piping Insulation
Guidelines
NOTE
: Use closed cell, neoprene insulation or equivalent.
The vent pipe may pass through unconditioned areas. The amount
of exposed pipe allowed is shown in Table 15.
1. Using winter design temperature (used in load calculations),
find appropriate temperature for your application and fur-
nace model.
2. Determine the amount of total and exposed vent pipe.
3. Determine required insulation thickness for exposed pipe
length(s).
4. When combustion air inlet piping is installed above a sus-
pended ceiling, the pipe
MUST
be insulated with moisture
resistant insulation such as Armaflex or other equivalent
type of insulation.
5. Insulate combustion air inlet piping when run in warm, hu-
mid spaces.
6. Install the insulation per the insulation manufacturer’s in-
stallation instructions.
NOTE
: Pipe length (ft. / M) specified for maximum pipe lengths
located in unconditioned spaces cannot exceed total allowable pipe
length as calculated from Table 16.
Configure the Furnace
CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
To route the vent pipe and combustion air pipe through the
furnace, the manufacturer supplied kit must be used. Failure
to properly seal the blower compartment from the furnace
vestibule could result in the circulation of carbon monoxide
throughout the structure. The vent pipe and combustion air
pipe must be a continuous pipe while passing through the
blower compartment. Seals supplied in this kit must be
installed per the instructions provided. Follow all
procedures outlined in these instructions.
WARNING
!
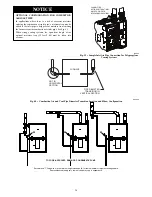
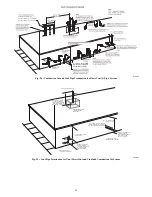
Near Furnace Vent Connections
Offsets in the vertical portion of the vent pipe should be made with
45 deg. elbows instead of 90 deg. elbows. Short horizontal runs of
vent pipe are difficult to pitch correctly and may trap water in the
vent pipe. Trapped water in the vent pipe may result in nuisance
pressure switch tripping.
A14546
Fig. 42 -- Near Furnace Vent Connections
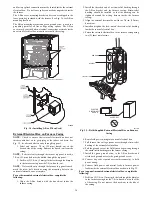
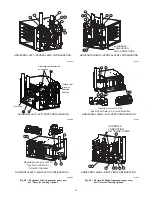
Install the Vent and Combustion Air Pipes
With the furnace installed in the required position, remove the
desired knockouts from the casing. It will be necessary to remove
one knockout for the vent pipe and the other knockout for the
combustion air connection. See Fig. 13.
Use a flat blade screwdriver and tap on the knockout on opposite
sides, where the knockout meets the casing. Fold the knockout
down with duct pliers and work the knockout back and forth until
it is removed. Trim any excess metal from the knockout with tin
snips.
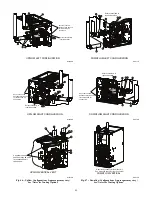
The vent elbow can be rotated to the required location on the
casing if necessary. See Fig. 43. To rotate the vent elbow:
1. Loosen the clamp on the inlet of the vent elbow attached to
the inducer.
2. Rotate the vent elbow to the required position. There are
rounded notches on the vent elbow to align it with the
inducer housing for each orientation.
3. Tighten the clamp around the vent elbow. Torque the clamp
to 15 lb--in. See Fig. 46--49.