8
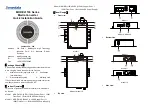
Inlet and Outlet Check Valves
A set of six (6) inlet and outlet check valves work in
conjunction with the pump pistons to create volume flow.
As a piston is moved toward the axial cam by its return
spring during its suction stroke, that piston’s inlet check
valve opens and allows water to enter the pumping
chamber. During the suction stroke, that piston’s outlet
check valve is forced closed, as depicted in Figure 2.2.
When the piston is pressed forward by the axial cam on its
pressure stroke, its inlet check valve is forced closed and its
outlet check valve is forced open, as seen in Figure 2.3.
Unloader - Pressure Regulator
Output water pressure can be adjusted using the pressure
adjust knob on the Unloader-Pressure Regulator assembly.
Turn the knob clockwise to increase pressure (up to the
rated maximum pump pressure), counterclockwise to
decrease pressure.
The pressure washer is provided with an unloader -
pressure regulator valve to protect the pump and hose
system whenever water flow is blocked upstream. Blockage
is caused when the spray gun trigger is normally closed or
by a kinked pressure hose or a clogged nozzle. Without an
unloader system, water pressure could increase until the
engine stalls or part of the system ruptures to relieve the
pressure.
As shown in Figure 2.4, the unloader valve will open at a
preset maximum pressure to divert all or part of the flow
back to the pump inlet. During such shutdown conditions,
the water will circulate from the pumping chambers to the
pump inlet and then back to the pumping chambers.
Section 2 • Pressure Washer Components
Portable Pressure Washer Familiarization and Troubleshooting Guide
Figure 2.4 — Typical Unloader - Pressure Regulator System
Figure 2.2 — Inlet Check Valve - Suction Stroke
Figure 2.3 — Outlet Check Valve - Pressure Stroke
Item
Name
1
Inlet check valve
2
Outlet check valve