Tungsten tip preparation
= Diameter
Taper length
2–3x Dia
Flat
1/4–1/2x Dia
DCSP (EN) or DCRP (EP)
Max. ball
1x Dia
ACHP General Purpose
Ball tip by arcing on clean metal at low current DCRP
(EP) then slowly increase current to form the desired ball
diameter. Return setting to AC.
Tungsten extension
General
purpose
3x Dia
Standard Parts
General
purpose
3x Dia
Maximum
6x Dia
Gas Lens Parts
(in draft free areas)
Tungsten electrode tip shapes and current ranges
Thoriated, ceriated, and lanthanated tungsten electrodes do not ball as readily as pure or zirconiated
tungsten electrodes, and as such are typically used for DCSP welding. These electrodes maintain a ground
tip shape much better than the pure tungsten electrodes. If used on AC, thoriated and lanthanated
electrodes often spit. Regardless of the electrode tip geometry selected, it is important that a consistent
tip configuration be used once a welding procedure is established. Changes in electrode geometry can
have a significant influence not only on the weld bead width, depth of penetration, and resultant quality,
but also on the electrical characteristics of the arc. Below is a guide for electrode tip preparation for a
range of sizes with recommended current ranges.
Electrode diameter
(mm)
Diameter arc tip
(mm)
Constant included
angle, (degrees)
Current range
(A)
1.0
0.125
12
2 – 15
1.0
0.250
20
5 – 30
1.6
0.500
25
8 – 50
1.6
0.800
30
10 – 70
2.3
0.800
35
12 – 90
2.3
1.100
45
15 – 150
3.2
1.100
60
20 – 200
3.2
1.500
90
25 – 250
Tungsten grinding
Shape by grinding longitudinally
(never radially). Remove the
sharp point to leave a truncated
point with a flat spot. Diameter
of flat spot determines amperage
capacity (See below). The
included angle determines weld
bead shape and size. Generally,
as the included angle increases,
penetration increases and bead
width decreases. Use a medium
(60 grit or finer) aluminium
oxide wheel.
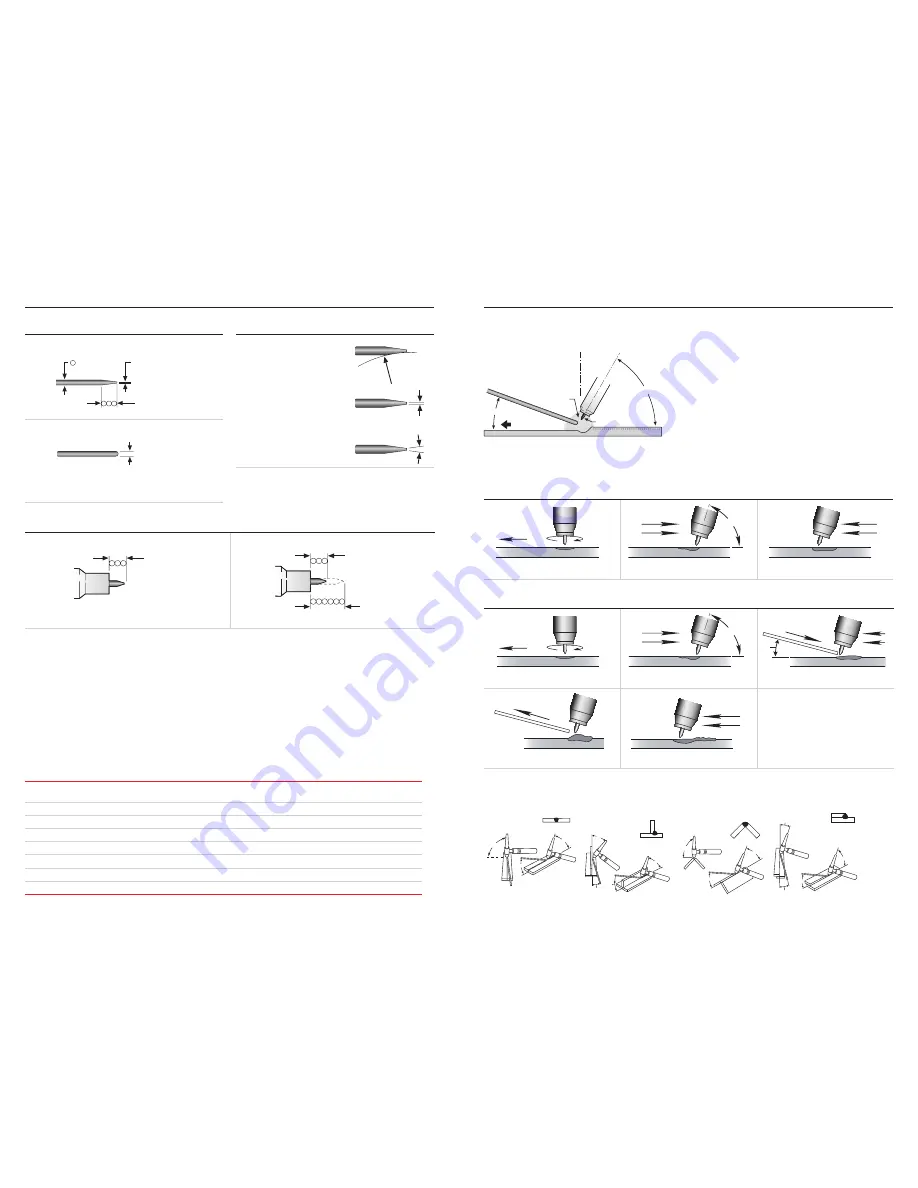
2.7 Welding techniques
60–75°
15–30°
Nozzle
Direction of travel
Welding Rod
Shield gas
Vertical
Tungsten electrode
The suggested electrode and welding rod angles
for welding a bead on plate. The same angles are
used when making a butt weld. The torch is held
60–75° from the metal surface. This is the same as
holding the torch 15–30° from the vertical.
Take special note that the rod is in the shielding
gas during the welding process.
2.8 Torch movement during welding
Tungsten Without Filler Rod
75°
75°
15°
Welding
direction
Form pool
75°
75°
15°
Tilt torch
75°
75°
15°
Move torch to front of pool. Repeat.
Tungsten With Filler Rod
75°
75°
15°
Welding
direction
Form pool
75°
75°
15°
Tilt torch
75°
75°
15°
Add filler metal
75°
75°
15°
Remove rod
75°
75°
15°
Move torch to front of pool. Repeat.
2.9 Positioning torch tungsten for various weld joints
Butt Weld and
Stringer bead
‘T’ Joint
Corner Joint
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
15°
75°
90°
20-40°
30°
15°
75°
90°
20°
70°
20°
10°
15°
75°
Lap Joint
BOC Smootharc TIG 185 Operating Manual
12
13
BOC Smootharc TIG 185 Operating Manual















